-

Cell-to-Cell Communication - Osseointegration
Stadlinger, Bernd / Terheyden, HendrikThe invisible becomes visible and holds both challenge and fascination. The cellular-level biological processes that underlie osseointegration are visualized based on the cell types and messengers implicated, representing the current state of our knowledge. Complex biodynamic processes are showcased dramatically and didactically to support the transfer of knowledge in training and education. Module 1, Cell-To-Cell Communication - Osseointegration, ushers in an Initiative for Excellence entitled Education - Science Comes Alive. It will eventually present all the relevant biomedical processes in dentistry and oral and maxillofacial surgery in the form of 3D animations, to be made available to a professional public as a 3D film library. This innovative genre - with special highlights for every viewer - will open up interesting teaching and training perspectives. Outline: - Hemostasis - Inflammatory Phase - Proliferative Phase - Remodeling Phase. On This Film Main Cast: Platelets, Fibroblasts, Endothelial Cells, Granulocytes, Macrophages, Pericytes, Osteoclasts, Osteoblasts, Osteocytes Also Starring: PDGF, Thromboxane, TGF - a, TGF - ß, VEGF, NO, ACE, TNF - a, IL - 1, IL - 6, FGF, MIP - 1, RANKL, Sclerostin Length: 12 minutes Project/Expert Team Authors and Scientific Management: Bernd Stadlinger, PD Dr. Dr. | Hendrik Terheyden, Prof. Dr. Dr. Advisory Board: Lyndon F. Cooper, DDS, PhD | Christoph Hämmerle, Prof. Dr. Thomas Hoffmann, Prof. Dr. | Myron Nevins, DDS Technical Advisors: Susanne Bierbaum, Dr. | Uwe Eckelt, Prof. Dr. Dr. Ute Hempel, Dr. | Lorenz Hofbauer, Prof. Dr. Dieter Scharnweber, Prof. Dr. (Transregio 67) -

Bone augmentation in the anterior region in preparation for implants
Grunder, UeliOutline: - Incision technique/flap mobilization - Bone removal with trephine cutter 6 mm - Bone bed preparation with trephine cutter 5 mm - Fixation of the autologous bone - Membrane adaptation - Introduction of the replacement material - Attachment of the membrane (with nails) - Introduction of a second membrane - Flap mobilization - Flap closure List of materials: - Trephine cutters (Biomet/3i, Palm Beach Gardens, Florida, USA) - Fixation screws (Biomet Microfi xation, Jacksonville, FL, USA) - e-PTFE membrane (Gore-Tex® reinforced, WL Gore, Flagstaff, AZ, USA ) - Mineralized collagen bone replacement material (Bio-Oss® Collagen, Geistlich Pharma AG, Wolhusen, Switzerland) - Collagen membrane (Biogide, Geistlich Pharma, Wolhusen, Switzerland) -

Preimplant Augmentation Procedures to Improve the Hard Tissue Situation in the Upper Anterior Region
Mayer, MatthiasContents - Flap design according to the layering technique - Piezoelectric bone surgery - Bone spreading with osteotomes - Augmentation and suturing Materials Checklist: Piezo surgery unit (ADS); Osteotome (Altatec GmbH); Surgical tray, individual. -

Clinical implant prosthodontics - step by step
Weigl, Paul / Trimpou, GeorgiaClinical steps for the fabrication of implant-supported restorations - Single-tooth restoration - Fixed partial denture - Electroplated cone-retained restoration - Conical copings using a pre-fabricated abutment matrix system -
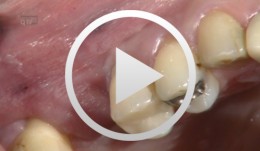

Augmentation at site 16 using the SonicWeld Rx System
Iglhaut, Gerhard M. -
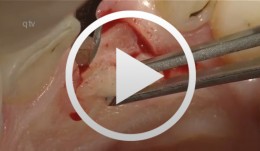

Immediate placement of a NobleActive implant in a patient with a pronounced hard-tissue and soft-tissue defect
Nölken, RobertOutline - Modified tubed flap - NobelActive implant placement - Flapless facial bone augmentation - Immediate provisionalization Materials Checklist: NobelActive™ Surgery Kit Twist drill ø 2, 7-15 mm Twist drill ø 2, 10-18 mm Twist step drill ø 2.4/2.8, 7-15 mm Twist step drill ø 2.4/2.8, 10-18 mm Twist step drill ø 3.2/3.6, 7-15 mm Twist step drill ø 3.2/3.6, 10-18 mm Surgical driver NobelActive™ Man torque wrench, surgical NobelActive™ Internal RP implant Procera® esthetic abutment, NobelActive™ Internal Implant replica, NobelActive™ Internal RP Impression coping, open tray, NobelActive™ Internal RP Protect analog, NobelActive™ Internal. -

-
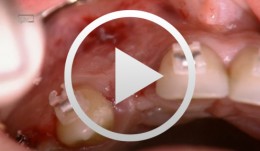

Navigated implantation and connective-tissue graft
Hienz, Stefan -
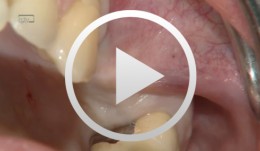

Re-entry at sites 24 and 25
Iglhaut, Gerhard M. -
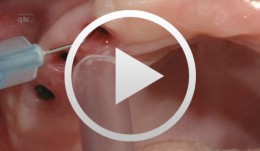

Clinical implant prothodontics - Part II
Weigl, Paul / Trimpou, Georgia -
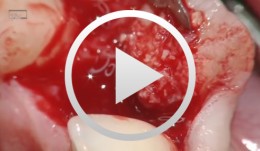

Anterior implant with concurrent bone augmentation (GBR)
Grunder, UeliOutline: - Incision technique/flap mobilization - Implant insertion - Membrane adaptation - Introduction of the replacement material - Attachment of the membrane - Introduction of the second membrane - Flap mobilization - Flap closure List of materials: Titanium implant (Thommen Medical, Waldenburg, Switzerland); e-PTFE membrane (Gore-Tex® reinforced, WL Gore, Flagstaff, AZ, USA); Mineralized collagen bone replacement material (Bio-Oss® Collagen, Geistlich Pharma, Wolhusen, Switzerland); Collagen membrane (Biogide, Geistlich Pharma, Wolhusen, Switzerland) -
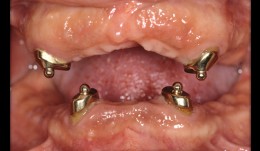

Esthetic improvement in implant-supported fixed and removable dentures
Christian RamelHow to improve esthetics and stability of implant-supported fixed and removable dentures.