-
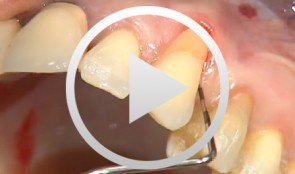
Covering a Recession with a Soft Tissue Transplant
Heinz, Bernd / Jepsen, SörenObjectives: Use of a soft tissue graft for recession coverage at tooth 23 and for gingival augmentation. Content: 1. Incision around tooth 23, intra-sulcular preparation, mobilization of coronal sliding flap, and pre-flap preparation. 2. Root smoothing, reduction of ground cavity with diamond burs from Perioset system. 3. Preparation and harvesting of connective tissue flap from palate, Emdogain application, and wound closure. 4. Placement of interrupted interdental sutures for fixation of connective tissue flap. -

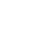
Core & Post System Post Cementation and Core Build Up
Nölken, RobertMaterials Checklist: Dentsply Core&Post system kit. -
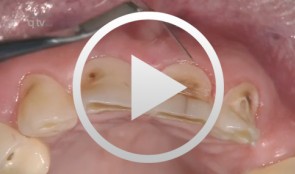

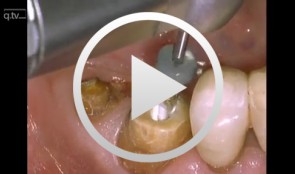
Veneer preparation in cases with wedge-shaped defects
Kopsahilis, NikolaosContents: - Medical history and diagnosis - Dental status, periodontal status, functional status - Periodontal therapy, functional therapy - Conservative treatment - Restoration (a: posterior; b: anterior) Materials Checklist Sutures: - Gingi-Plain - Z-Twist - Non-impregnated (Gingi-Pak) Impression materials: - Impregum Penta Soft (3M ESPE) - Permadyne Garant 2:1 (3M ESPE) -
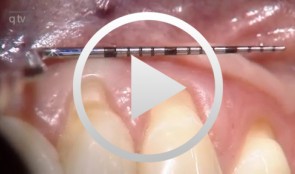

Recession coverage using human dermal tissue at site 22-26
Schlee, Markus -
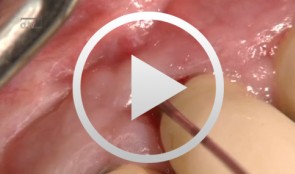

Laser decontamination at sites 11 and 12
Schwarz, FrankOutline: - Presentation of clinical findings - Explanations Er:YAG laser/fibre tip/power settings - Treatment - Postoperative management List of materials: Er:YAG laser device (KEY 3®, KaVo, Biberach, Germany) Laser handpiece (2061, KaVo, Biberach, Germany) Cone-shaped glass fibre tip Safety goggles Periodontal probe (PCP12, Hu-Friedy Co., Chicago, Illinois, USA) -
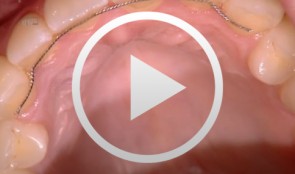

Recession coverage with connective tissue using the envelope technique at site 13
Ratka-Krüger, PetraList of materials: Periodontometer, handle #6 (Hu-Friedy); Universal probe, handle #6 (Hu-Friedy); Mirror handle #6 (Hu-Friedy); Transfer handle, round; Respiratory, Hirschfeld; Surgical curettes, Prichard; Universal curettes, Younger-Good, handle #6; Universal curette, Indiana University, handle #6; Universal curette, Langer After-Five, handle #6; Tweezers, Gerald; Tweezers, fine; Spatula, fine; Tissue cutter, Super-Cut; Thread cutter, Godman-Fox; Needle holder, Lichtenberg; Needle holder, Castroviejo; Hemostat; Scalpel blades; Tunneling instruments; Gingivectomy meter, Orban, handle #6; Blade holder, Universal 360°; Suture material, polypropylene C6; Suture material, polypropylene C17. -
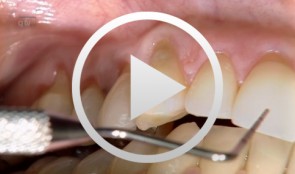

Recession coverage with coronally positioned flap
Zucchelli, GiovanniOutline: - Aesthetic treatment of multiple gingival recessions List of materials Microblade BUSM-6700 (Stoma) and 15C Swan Morton, Periosteum elevator Free, De Wijs, Molt (Stoma), Curettes minifive 11-12, 7-8 (LM), Pinzette stright 17cm 0,6 (stoma), Neddle holder micro Barraquer straight 18cm extra fine (stoma), Micro-scissor Gomel, curve, 16cm extra fine (stoma), Suture Vicryl 6-0 (V384) -
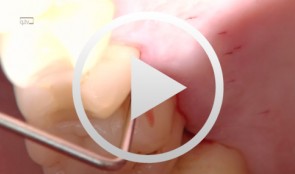

Treatment of a palatal class II furcation
Marggraf, ErwinOutline: - Reflecting a flap - Cleaning. - Fraction 3 - Fraction 2 - Fraction 1 - Wound closure List of materials All materials required for producing PRGF (BTI Germany) Bone replacement materials Geistlich Biomaterials Surgical instruments, Aesculap Suture materials, Ethicon -
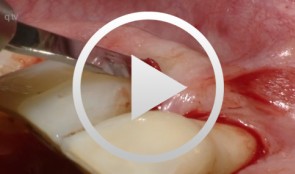

Flap surgery using a modified papilla preservation technique
Salvi, Giovanni E.Outline - Introduction: Patient history, clinical findings, diagnoses, etiology, prognosis of individual teeth - Treatment planning for phases - Modified papilla preservation technique (MPPT) - Simplified papilla preservation technique (SPPT) -Clinical situation 6 months postoperatively -

Operative Therapiekonzepte zur Entfernung retinierter unterer Weisheitszähne
Schultze-Mosgau, Stefan / Neukam, Friedrich Wilhelm / Basting, GerdGliederung: - Schematische und röntgenologische Demonstration unterschiedlicher Retentionsformen unterer, retinierter Weisheitszähne, Darstellung der Indikation zur Entfernung - Erstellung der Behandlungsunterlagen, Aufklärungsgespräche mit Darstellung der Komplikationen - Demonstration des operativen Vorgehens: Lokalanästhesie, Schnittführung, Schutz des N. lingualis, Osteotomie, Nahttechnik. Die Entfernung unterer, retinierter Weisheitszähne gehört zu den häufigsten dento-alveolär-chirurgischen Eingriffen. Durch die enge anatomische Lagebeziehung zu den benachbarten Zähnen und dem N. alveolaris inferior besteht bei der operativen Entfernung die Gefahr einer Schädigung der umgebenden Strukturen. Die Kenntnis der verschiedenen Retentionsformen und eine geeignete, atraumatische Operationstechnik ist für eine komplikationslose Entfernung von Bedeutung. Nach der Leitungsanästhesie des N. alveolaris inferior und des N. buccalis wird die Schnittführung so gewählt, dass ein vestibulär gestielter Mukoperiostlappen gehoben werden kann. Nach dem lingualen, subperiostalen Einführen eines Raspatoriums zum Schutz des N. lingualis wird durch die bukkale Osteomie mit kugelförmigen Hartmetallfräsen der Weisheitszahn bis zu seiner größten Zirkumferenz freigelegt und durch vorsichtige Luxationsbewegungen entfernt.