-
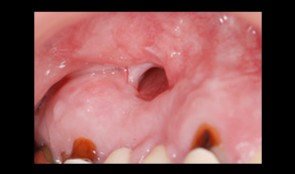

Total reconstruction after closure of maxillary sinus fistula
Dr. Thomas TruningerBefore starting the full-mouth reconstruction, the oral-maxillary sinus fistula (oroantral fistula) has to be closed. -
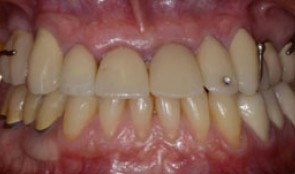

Tendency of skeletal class 3 and a missing front tooth
Dr. Dominik BüchiIn this clinical case session you are going to learn how to plan and execute treatment in a partially edentulous patient situation applying implants within the overall reconstructive treatment concept. In particular you will learn the importance of the preparatory phases of therapy and to plan and treat with the prosthetic aim in mind. -
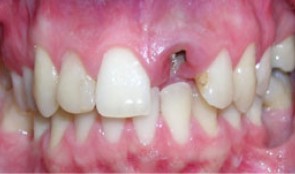

Single implant crown in the esthetic zone
Dr. Vladimir KokovicMale patient *1986 by Dr. V. Kokovic (02-10/2007). Anterior single implant placement after orthodontic extrusion and ridge preservation. -
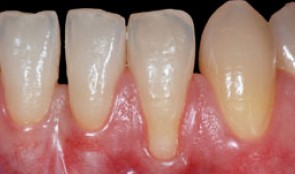

Root coverage with tunnel technique
Ignacio Sanz MartinRecession on tooth 32. Connective Tissue graft with tunnel technique for root coverage. -
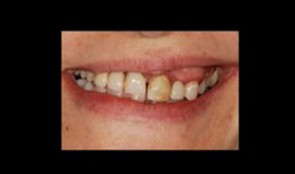

Replacement of poorly fitting removable prosthesis and simultaneous orthodontic treatment
Dr. Dominik BüchiThis patient (*1971) treated by Dr. Büchi, came to our clinic for a replacement of her poorly fitting removable prostheses. Additionally severe orthodontic problems, i.e. a slanting occlusion plane are bothering the patient and are in need of treatment. -
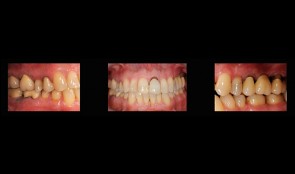

Rehabilitation of masticatory performance in a patient with periodontitis
Dr. Dominik BüchiFemale patient (*1948) suffering from periodontitis wants to reach a state of complete oral health and ideal masticatory performance. -
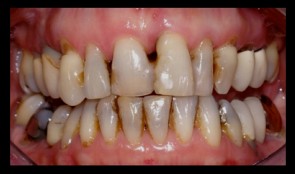

Periodontitis case, smoker, shortened dental arch, reconstructions on implants
Prof N. P. Lang and M. Lulic.Female patient *1951 by M. Lulic. N. P. Lang (2006-2008). Periodontitis case, smoker, shortened dental arch, reconstructions on implants (3-unit bridge and single crown). -
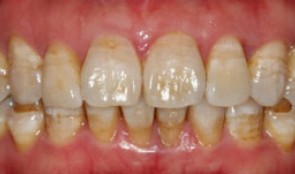

Periodontitis case, single implant crown
Prof. Niklaus Lang and J. TamMale patient *1970, by J. Tam and N. P. Lang (2011-2013), University of Hongkong. Periodontitis case with pain and furcation involvement, single implant crown -
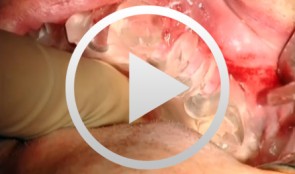

Sinus Bone Augmentation with PRP
Schultze-Mosgau, StefanContents - Incision technique for lateral sinus floor augmentation - Creation of a lateral bone window in the facial maxillary sinus wall - Maxillary sinus floor elevation - Chin bone graft harvesting - Retromolar bone harvesting - Sinus floor augmentation using autologous bone, beta- tricalcium phosphate (1:1) and PRP Synopsis: Maxillary sinus augmentation may be indicated in cases where it is desirable to increase the vertical bone stock in the upper lateral tooth region. Maxillary sinus floor augmentation entails the implantation of autologous bone or bone replacement material in the spaces between the bony floor and elevated membrane of the maxillary sinus. This video demonstrates the techniques for palatal incision, access preparation, and exposure of the facial wall of the maxillary sinus. A diamond drill is used to create a bony window in the facial wall of the maxillary sinus taking care not to perforate the sinus membrane. After completely detaching the basal parts of the membrane, the flap is advanced cranially using angular elevation instruments. Regarding the procedure for autologous bone grafting, the steps for incision, prepping and harvesting of monocortical chin bone transplants with a trephine drill are demonstrated. An alternative procedure for harvesting retromolar bone material is also shown. A bone mill is used to particulate the autologous bone material. The autologous bone chips are then mixed 1:1 with beta-tricalcium phosphate (and PRP) and inserted in the sinus floor. -
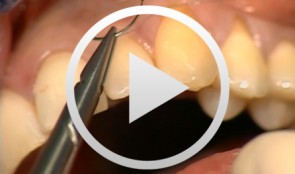

Esthetic Periodontal Treatment with Microsurgical
Wachtel, HannesContents - Instruments and planning - Incision - Split thickness flap preparation - Harvesting connective tissue for grafting - Palatal sutures - Transplant insertion and suture - Microsurgical suture Synopsis: Microsurgical operation to repair two adjacent, exposed root surfaces. The video demonstrates step-by-step how to prepare a coronally advanced split-thickness flap with subepithelial connective tissue. To remove connective tissue from the palate, a horizontal incision is required. Ultra-precise microsurgical suturing is the key to obtaining aesthetically perfect results.