-
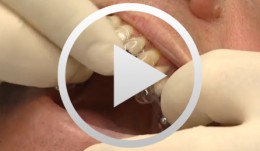

Ballon Lift Control - A life report
Heuckmann, Karl-Heinz -
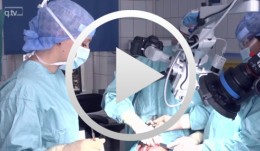

Microsurgical lateral sinus floor elevation (LSFE)
Nölken, RobertOutline: - Incision - Flap mobilization - Lateral sinus fenestration - Elevation of the Schneiderian membrane - Implant bed preparation - Bone chip harvesting at the mandibular angle - Filling of sinus lift lumen with autologous bone chips - Implant insertion - Covering the lateral sinus cavity with collagen membrane - Wound closure List of materials - Zeiss Pro Dent microscope with beam splitter and Panasonic 3 CCD camera - Scalpel holder (Ustomed) with Swann-Morton blades 15C and 12D - Narrow rasp (Hu-Friedy) - Micro-vacuum (Luer Lock Suction Tip, American Dental Systems) - Disposable vacuum tube set (Bexamed) - Disposable draping, Lindau (Aescologic) - Piezosurgery with diamond ball (Mectron) - Microforceps (Hu-Friedy) - Excavator (Martin) - Periodontometer, 1-mm gradation (Hu-Friedy) - OsseoSpeed implant set, Dentsply Implants: Marking drill; Twist drill, 2 mm; Depth gauge; Pilot drill, 2/3.2 mm; Twist drill, 3.2 mm; Tapered drill, 3.2/5 mm; OsseoSpeed TX implant, 5.0 × 11 mm; Closure screw, 4.5/5 mm - Columbia curette (Ustomed) - Micross scraper (Meta) - Needle holder (Ustomed) - Langenbeck wound retractor (Ustomed) - Kelly scissors (Ustomed) - Buchanan endodontic hand plugger (American Dental Systems) - Resorbable collagen membrane (Resodont, Resorba) - Ethilon 5-0 FS-3 (Ethicon) - Prolene 6-0 DA-2 (Ethicon) -
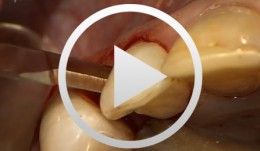

Regenerative Measures for Osseous Defect Repair and Optimal Esthetics
Sculean, AntonProcedure: Theoretical Part: - Adult male with a deep and broad intraosseous bone defect located on tooth #13 - The indication for modified papilla preservation in the scope of regenerative therapy was established based on the width of the diastema - Regenerative periodontal therapy with Emdogain and a Bio-Oss® cancellous bone graft - Emdogain is applied to the root surface to stimulate regeneration of periodontal structures - To prevent graft collapse and to minimize the risk of development of too large a recession in this esthetically important region, the defect was filled with Bio-Oss® cancellous bone material Practical Part: - The papilla preservation technique was performed using microsurgical instruments - The root surface area was conditioned with 24% EDTA for ca. 2 minutes - Emdogain was applied to the root surface - The defect was filled with the Emdogain/Bio-Oss® mixture - The wound was closed with two mattress sutures one horizontal mattress suture to secure the graft in place, and a second modified vertical mattress suture to tightly close the papilla - A 5-0 suture was used for the horizontal mattress suture, and a 6-0 monofilament was used for the vertical mattress suture - Postoperative care entailed rinsing the wound twice daily for 4 weeks with 0.2% chlorhexidine and ibuprofen analgesia on the first few days after surgery Contents: The patient's jaw displayed a generalized loss of clinical attachment and alveolar bone. His general history was unremarkable; the patient was a non-smoker. Microbiological tests showed large numbers of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans and Porphyromonas gingivalis. The diagnosis was "generalized aggressive periodontitis". After four months of initial therapy consisting of antibiotic combination therapy (amoxicillin + metronidazole), intraoral radiographs showed a deep and wide intraosseous bone defect located mesial and palatal to tooth #13. To preserve this strategically important tooth we opted to perform regenerative therapy with Emdogain and Bio-Oss cancellous bone material. Ten months after regenerative periodontal therapy, the probing depth had decreased by 7 mm, and 5-6 mm of clinical attachment had been gained. At this time, the probing depth was 2-3 mm and intraoral radiographs showed near-complete filling of the osseous defect. -
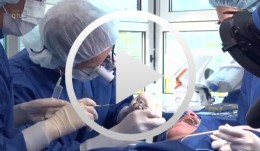

-

Cell-to-Cell Communication: Periodontal Regeneration
Stadlinger, Bernd / Terheyden, HendrikUnlike bone, which undergoes remodeling by resorption followed by bone apposition, teeth are not subject to physiological remodeling. They are remarkably resistant to physiological remodeling processes. The reason for this is found in the periodontium and cementum. The mechanisms that take effect in this area and the effectiveness of the periodontal system - consisting of gingiva, alveolar bone, periodontium and cementum - after injuries will be visualized in the new scientific 3D film, "Periodontal Regeneration".The visualization of these complex processes is of great interest for academic teaching as well as for the clinician and general practitioner as the cellular interactions are presented in the context of four phases. For the first time scanning electron microscopic images of real cells will be visualized allowing the comparison of their characteristics with computer animated simulations. DVD 1: Expert Version approx. 14 minutes DVD 2: Public Version approx. 13 minutes Outline: - Cementum formation - Orthodontic tooth movement - Trauma and periodontitis - Periodontal regeneration -
Periodontal Preserve Therapy (Examples)
Clotten, StefanContent: - Periodontal maintenance therapy for teeth 34 and 35, including the regeneration of a bone defect using bone replacement material, collagen membrane and sutures. - Curettage for treatment of periodontal pockets. - Treatment of gingival pressure sores caused by tight-fitting orthodontic apparatus. - Incision of buccal attachment to relieve gingival pressure for elimination of gingival recession. -

Treatment of a palatal class II furcation
Marggraf, ErwinOutline: - Reflecting a flap - Cleaning. - Fraction 3 - Fraction 2 - Fraction 1 - Wound closure List of materials All materials required for producing PRGF (BTI Germany) Bone replacement materials Geistlich Biomaterials Surgical instruments, Aesculap Suture materials, Ethicon -


The use of autologous PRGF in periodontal plastic surgery
Marggraf, ErwinContents: - Blood sampling - Platelet separation activation - Introduction of bone replacement material - Access flap and curettage - Introduction of PRGF and bone replacement material - Plastic suture Materials Checklist: All materials required for producing PRGF (BTI Germany) Bone replacement materials Geistlich Biomaterials Surgical instruments, Aesculap Suture materials, Ethicon -
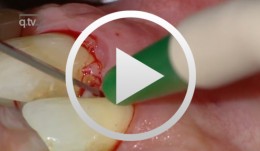

Periodontal regeneration at teeth 21 and 23 using EMD and cortical bone chips
Topoll, Heinz H.Contents: - Incisions using a microsurgical scalpel - Reflecting a buccal flap - Preparing papillary flaps using a microsurgical scalpel - Lifting off of the papillary flaps using a papillary elevator - Removing the granulation tissue using an ultrasound scaler - Cleaning the dental roots using manual instruments - Trying to dental root - Applying Emdogain - Mixing Bio-Oss and Emdogain - Introducing the Bio-Oss into both bone defects - Microsurgical suturing Materials Checklist: Cheek retractor Microsurgical scalpel blade holder Microsurgical scalpel blade Soniflex tips Bone rest Castroviejo microsurgical needle holder Suturing scissors Dental tweezers Microsurgical tweezers Monofilament suturing material 6/0 Seralene Pref gel Emdogain Bio-Oss -
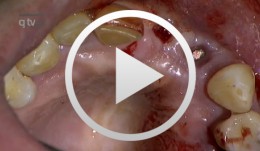

Ridge augmentation in the periodontally involved dentition
Windisch, PéterContents: - Periodontal regeneration and alveolar -ridge augmentation using a connectivetissue graft - Implant insertion and augmentation - Implant re-entry and prosthetics Materials Checklist Emdogain, Bio-Oss, BioGide, Block fixating screw for autologous bone cylinder, 4/0 and 5/0 sutures, Resolut membrane Titanium pins, Autologous bone chips, 2 Replace Groovy Tapered 4, 3x13 mm implants -

Defect Prevention following Extraction of a Maxillary Central Incisor
Zuhr, OttoContents: - Minimally invasive, atraumatic extraction of an anterior tooth - Buccal soft tissue augmentation using a modified tunneling technique - Socket preservation technique for conservation of the extraction socket - Provisional restoration and closure using modified suspension sutures Materials Checklist: Tunneling Knife® (Dr. Zuhr), No. 1 / No. 2 Keydent Microblade SR Geistlich Bio-Oss® Spongiosa, particle size 0.25 - 1 mm Geistlich Bio-Gide® membrane, 25 x 25 mm Seralene Blue 7/0 DS-15, 0.5 m sutures CV-5 Gore-Tex sutures -


Sinus Floor Augmentation with Autogenous Chin Bone Grafts
Schultze-Mosgau, Stefan / Neukam, Friedrich Wilhelm / Basting, GerdContent: In the maxillary incisor region, a sinus floor augmentation to enlarge the vertical bone supply may be indicated for a vertically reduced local bone height of less than 5 to 7 mm before procedures to rehabilitate masticatory function with an implant-bearing tooth replacement. For a single-sided deposit osteoplasty, the quantity of autogenous bone from the chin region is usually sufficient. The operative procedure of a single-sided lateral sinus floor augmentation is demonstrated with particulate spongious bone and alternatively with an autogenous block graft. The video also shows the operative method for a crestal sinus floor augmentation with the aid of the endoscopically controlled condensation technique. The advantages and disadvantages of the individual procedures are highlighted. In addition, the technique for harvesting chin bone transplants in different case examples is shown. Outline: - Operative technique for lateral sinus floor augmentation with autogenous particulate spongious bone - Operative technique for lateral sinus floor augmentation with autogenous block grafts - Crestal, endoscopically controlled sinus floor augmentation with condensation technique - Techniques for harvesting chin bone grafts - Range of indication for sinus floor augmentation - Lateral sinus floor augmentation - Operative technique of crestal, endoscopically controlled sinus floor augmentation - Operative technique of autogenous chin bone removal