-
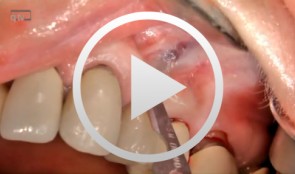

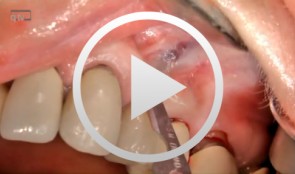
Microsurgical apical resection on a maxillary premolar
Nölken, Robert -
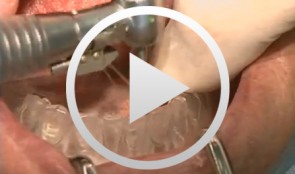

Implants for the Anterior Maxillary Region
Horrichs, Leon G.Contents: - Implant planning and positioning - Preparation - Drilling and thread-cutting - Implant insertion - Wound closure Synopsis: The implant position is determined using a drill guide/x-ray template (regions 34-32-42-44). A Peeso drill is inserted in the drill guide and used to mark the position in the mucoperiosteum. An incision is made, and the mucoperiosteum is displaced. The implant insertion sites are prepared by using a 2 mm twist drill, 2/3 mm pilot drill, 3 mm and 3/5 mm twist drills. This is followed by counter-drilling and thread-cutting. The implants were loaded at 40-50 N. The wound is then closed using GORE-TEX® suture material. -

-
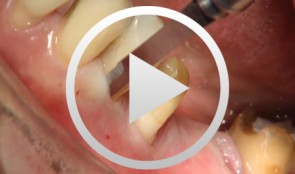
Periodontal Preserve Therapy (Examples)
Clotten, StefanContent: - Periodontal maintenance therapy for teeth 34 and 35, including the regeneration of a bone defect using bone replacement material, collagen membrane and sutures. - Curettage for treatment of periodontal pockets. - Treatment of gingival pressure sores caused by tight-fitting orthodontic apparatus. - Incision of buccal attachment to relieve gingival pressure for elimination of gingival recession. -

-


Sinus Floor Augmentation with Autogenous Chin Bone Grafts
Schultze-Mosgau, Stefan / Neukam, Friedrich Wilhelm / Basting, GerdContent: In the maxillary incisor region, a sinus floor augmentation to enlarge the vertical bone supply may be indicated for a vertically reduced local bone height of less than 5 to 7 mm before procedures to rehabilitate masticatory function with an implant-bearing tooth replacement. For a single-sided deposit osteoplasty, the quantity of autogenous bone from the chin region is usually sufficient. The operative procedure of a single-sided lateral sinus floor augmentation is demonstrated with particulate spongious bone and alternatively with an autogenous block graft. The video also shows the operative method for a crestal sinus floor augmentation with the aid of the endoscopically controlled condensation technique. The advantages and disadvantages of the individual procedures are highlighted. In addition, the technique for harvesting chin bone transplants in different case examples is shown. Outline: - Operative technique for lateral sinus floor augmentation with autogenous particulate spongious bone - Operative technique for lateral sinus floor augmentation with autogenous block grafts - Crestal, endoscopically controlled sinus floor augmentation with condensation technique - Techniques for harvesting chin bone grafts - Range of indication for sinus floor augmentation - Lateral sinus floor augmentation - Operative technique of crestal, endoscopically controlled sinus floor augmentation - Operative technique of autogenous chin bone removal -

Defect Prevention following Extraction of a Maxillary Central Incisor
Zuhr, OttoContents: - Minimally invasive, atraumatic extraction of an anterior tooth - Buccal soft tissue augmentation using a modified tunneling technique - Socket preservation technique for conservation of the extraction socket - Provisional restoration and closure using modified suspension sutures Materials Checklist: Tunneling Knife® (Dr. Zuhr), No. 1 / No. 2 Keydent Microblade SR Geistlich Bio-Oss® Spongiosa, particle size 0.25 - 1 mm Geistlich Bio-Gide® membrane, 25 x 25 mm Seralene Blue 7/0 DS-15, 0.5 m sutures CV-5 Gore-Tex sutures -

Periodontal regeneration at teeth 21 and 23 using EMD and cortical bone chips
Topoll, Heinz H.Contents: - Incisions using a microsurgical scalpel - Reflecting a buccal flap - Preparing papillary flaps using a microsurgical scalpel - Lifting off of the papillary flaps using a papillary elevator - Removing the granulation tissue using an ultrasound scaler - Cleaning the dental roots using manual instruments - Trying to dental root - Applying Emdogain - Mixing Bio-Oss and Emdogain - Introducing the Bio-Oss into both bone defects - Microsurgical suturing Materials Checklist: Cheek retractor Microsurgical scalpel blade holder Microsurgical scalpel blade Soniflex tips Bone rest Castroviejo microsurgical needle holder Suturing scissors Dental tweezers Microsurgical tweezers Monofilament suturing material 6/0 Seralene Pref gel Emdogain Bio-Oss -


The use of autologous PRGF in periodontal plastic surgery
Marggraf, ErwinContents: - Blood sampling - Platelet separation activation - Introduction of bone replacement material - Access flap and curettage - Introduction of PRGF and bone replacement material - Plastic suture Materials Checklist: All materials required for producing PRGF (BTI Germany) Bone replacement materials Geistlich Biomaterials Surgical instruments, Aesculap Suture materials, Ethicon -

Recession coverage using human dermal tissue at site 22-26
Schlee, Markus