-

Study Protocols: Vertical Ridge Augmentation
based on the book chapter by Isabella Rocchietta, David Nisandand Massimo Simion Summary This chapter reviews the need for standardized research into vertical ridge augmentation procedures because restoring bone volume after trauma or disease is clinically challenging; the outcomes are unpredictable, the complication rates are high and success is limited. The presented protocol involves initial augmentation surgery comprising a composite graft of autogenous bone and deproteinized bovine bone, with tenting screws and a PTFE membrane overlay, followed 6 months later by surgical removal of the membrane and screws and placement of an implant. Guided bone regeneration is compared with a gold standard two-stage procedure using autogenous bone strips with deproteinized bovine particles and a titanium-reinforced membrane. The timeline incorporates a 6-month evaluation phase and further evaluation 4 months later, with a 5-year follow-up. Patient numbers and selection criteria are defined, along with suitable endpoints, care routines and the use of cone-beam CT to assess bone gain and quality. The descriptions are illustrated by CT images, radiographs and clinical photographs that show preparation of the donor and implant sites in both surgical phases. The evaluation phase relates to responses of the defect over time in terms of resorption of graft particles, soft tissue swelling, inflammation, and bone destruction and formation. What the protocol aims to do is improve outcomes for patients with traumatic tooth extractions, jaw damage, endodontic infections and failed implants. Open full-text PDF (1.4 MB) -
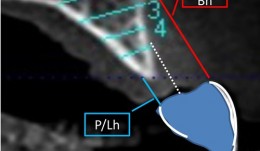

Study Protocols: Horizontal Ridge Augmentation
based on the book chapter by Nikos Donos and Nikos Mardas Summary This protocol focuses on measuring radiographic bone levels on the buccal side of augmented areas around implants after horizontal ridge augmentation, rather than at interproximal sites (a limitation of most published studies). The design offers a standardized means to assess graft materials, bone fillers and bone substitutes for horizontal ridge preservation, allowing comparisons of resorbable and non-resorbable materials and natural and synthetic membranes. It includes two randomized controlled trials for patients with bone defects from destructive gum disease who need local ridge augmentation before implantation. One trial uses a simultaneous technique whereby implants are placed in bone augmented with a new bone substitute plus a new or standard membrane, or a standard collagen membrane plus deproteinized bovine bone mineral; this trial comprises two phases surgical implantation and observation. The other trial is a staged technique comprising a new block-bone graft/substitute plus a new or standard membrane, and autogenous block bone graft plus a standard collagen membrane; this has a third phase. A 1-year timeline and 5-year follow-up is suggested for both trials. The authors cite various histologic and radiographic endpoints, photon bubble oscillations, peri-implant bone preservation, implant survival, patient morbidity, adverse events and patient-related outcomes. Images are provided of the change in bucco-palatal/lingual alveolar ridge width 6 months after the procedure. Open full-text PDF (1.3 MB) -

Study Protocols: Ridge Preservation
based on the book chapter by Suzanne Mason, Feng Wang, andDarnell Kaigler Summary This chapter explains the mechanisms of bone resorption and describes how to restore ridge deficiencies after tooth extraction and ensure a stable alveolar ridge for optimal implant survival, with a review of techniques and maintenance. The protocol was derived from a published study on the bone regeneration and stability after extraction of pre-molar or single-rooted anterior teeth. It defines the research question relating to a randomized controlled feasibility study, and cites how many patients are needed to undergo surgery. There are two treatment arms: one with autologous grafts using tissue repair cells (TRC) such as macrophages and mononuclear cells, derived from the patients bone marrow aspirates; others receive guided bone regeneration. The design, illustrated by a CONSORT diagram and clinical images of the procedures, incorporates phases for grafting/bone healing, implant osseointegration and biomechanical loading/restoration, with a 6-month follow-up consisting of postoperative care, specified evaluations and adverse-event recording. Primary and secondary endpoints are clearly defined, with assessments by CT, radiography, histology, the Misch bone density scale and torque testing. The recommended analysis is by KaplanMeier survival curves. The authors address the limitations of stem cell techniques, their isolation and expansion, and of transplantation of cells and grafts. Because biologicals are used, the authors recommend forming a data safety monitoring board (DSMB). Open full-text PDF (1.4 MB) -

-
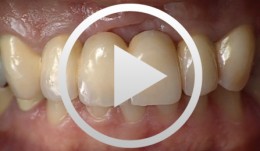

Implant Bone Dentures with Bone Augmentation and Soft Tissue Transplantation for Papillary Regeneration (Clinic and Laboratory)
Körner, Gerd / Müterthies, KlausDrill guide preparation with the aid of a temporary; Bone augmentation using a bone block graft; Implant insertion; Augmentation of gingival margin with a soft tissue graft from the roof of the mouth; Preparation of tooth replacements according to esthetic criteria, in some cases, as all-ceramic crowns. -
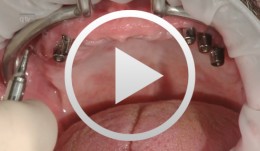

Clinical implant prosthodontics - Part III
Weigl, Paul / Trimpou, Georgia -

-
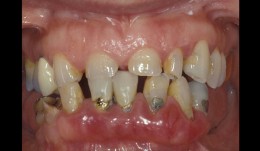

Full reconstruction of lower jaw inculding esthetic improvement
PD Dr. Ronald JungTo create optimal chewing efficiency the lower jaw was reconstructed with mixed implant- and tooth-supported bridges containing cantilevers. The abraded front teeth were crowned to improve the esthetics. -
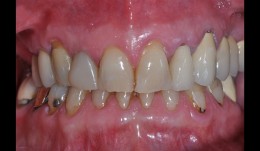

Fixed reconstructions in upper and lower jaw
Dr. Sven MühlemannFixed tooth- and implant-supported reconstructions in upper and lower jaw. Case treated by Dr. Sven Mühlemann, University of Zürich -
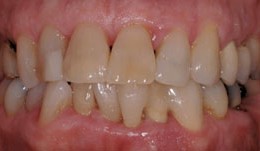

Fixed reconstruction
PD Dr. Ronald JungTooth-borne and implant supported FDPs and an adhesive bridge in combination with orthodontic treatment in lower front teeth. -
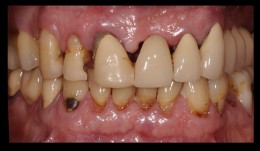

Extensive replacement of old and insufficient restorations
Dr. Dominik BüchiThis patient treated by Dr. Büchi came to our office because he was bothered by the low esthetics and masticatory performance of his dental works. -
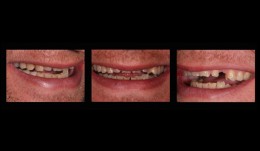

Esthetic rehabilitation in patient with myoarthropathy
Dr. Dominik BüchiMale patient (*1969) with myoarthropathy is looking for an esthetic rehabilitation of his teeth, which are severely damaged by attrition, abrasion and erosion.