-
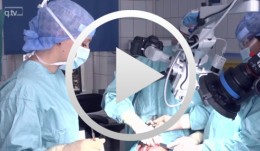

Microsurgical lateral sinus floor elevation (LSFE)
Nölken, RobertOutline: - Incision - Flap mobilization - Lateral sinus fenestration - Elevation of the Schneiderian membrane - Implant bed preparation - Bone chip harvesting at the mandibular angle - Filling of sinus lift lumen with autologous bone chips - Implant insertion - Covering the lateral sinus cavity with collagen membrane - Wound closure List of materials - Zeiss Pro Dent microscope with beam splitter and Panasonic 3 CCD camera - Scalpel holder (Ustomed) with Swann-Morton blades 15C and 12D - Narrow rasp (Hu-Friedy) - Micro-vacuum (Luer Lock Suction Tip, American Dental Systems) - Disposable vacuum tube set (Bexamed) - Disposable draping, Lindau (Aescologic) - Piezosurgery with diamond ball (Mectron) - Microforceps (Hu-Friedy) - Excavator (Martin) - Periodontometer, 1-mm gradation (Hu-Friedy) - OsseoSpeed implant set, Dentsply Implants: Marking drill; Twist drill, 2 mm; Depth gauge; Pilot drill, 2/3.2 mm; Twist drill, 3.2 mm; Tapered drill, 3.2/5 mm; OsseoSpeed TX implant, 5.0 × 11 mm; Closure screw, 4.5/5 mm - Columbia curette (Ustomed) - Micross scraper (Meta) - Needle holder (Ustomed) - Langenbeck wound retractor (Ustomed) - Kelly scissors (Ustomed) - Buchanan endodontic hand plugger (American Dental Systems) - Resorbable collagen membrane (Resodont, Resorba) - Ethilon 5-0 FS-3 (Ethicon) - Prolene 6-0 DA-2 (Ethicon) -
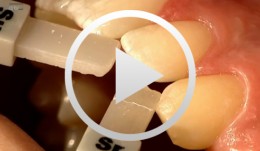

Composite Restoration in Anterior Teeth
Hugo, BurkardProcedure: - Introduction with control of the Gap Width and Colour Selection - Preparation of the Dental Surface (application of the Matrix) - Gap Closure, Final Polish Contents The present case shows the gap closure at tooth 22 with a direct adhesive technique. The gap closure is done here after the orthodontic treatment of a central diastema. A special matrix technique is used to allow a perfect design of the aproximal surfaces and the creation of the aproximal contact points. During the colour selection the dentin and enamel colours are chosen very carefully, to allow a good esthetic result and different composites are used to achieve a natural aspect of the tooth. -
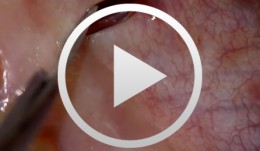

Regenerative Procedures for Optimized Esthetics at Tooth 11
Schlee, MarkusContents: - Exploration - Incision and Flap Mobilization - Palatal Flap Preservation with Interdental Tissue Preservation - Detoxification and Concrement Removal at 11 - Harvesting of Autogenous Bone Chips from the Spina Nasalis - Conditioning of the Root Surface with EDTA-Gel - Application of Emdogain and Filling of the Bone Defect - Wound Closure Synopsis After Finishing the Initial Treatment for Aggressive Periodontitis, Regenerative Treatment of a Tunnel-Shaped Pocket at Tooth 11 was attempted. Rotation and Crowding of the Buccally Inclined Tooth represented a favorable Etiological Factor. The patient did not wish to receive Orthodontic Treatment to eliminate this Causal Factor after Completion of Primary Treatment. Treatment was therefore limited to the Surgical Regeneration Attempt. The Interdental Space was larger than 3 mm and the Bone Pocket was a mostly Three-Walled Structure, so the Chances of Success were considered to be good. Exploration was first performed to identify the Course of the Defect Margins. Exact knowledge of the Bone Anatomy in all three Planes is essential to successful Incision Planning. A Tunnel-Shaped Defect delimited by Bone in the Region of Tooth 11 with good chances of Periodontal Regeneration was found. A major Challenge of this Procedure is the need to keep the Defect completely covered with Soft Tissue throughout the Healing Process. Cortellini's Papilla Preservation Technique was used for this Purpose. After Incision and Flap Mobilization, it became evident that the Defect only had two Walls in the Coronal Region and that Bone was lacking in the Buccal Region. According to the current Data on Periodontal Regeneration, the Attachment Gain achieved using an Enamel Matrix Protein (Emdogain®) alone can be just as good as that achieved using Emdogain and Bone Graft Material combined. Still, we elected to use a Combination Technique in the Present Case because it provides better Papillary Support. The Graft Material consisted of Autogenous Bone Chips from the Spina Nasalis, which can easily be harvested by Means of the Piezo Technique After gentle Detoxification, the Root Surface was treated with Emdogain. The Defect was then filled with Autogenous Bone Chips and closed by Microsurgical Suture Techniques. Six months after Surgery, Partial Regeneration of the Papilla can be seen. -
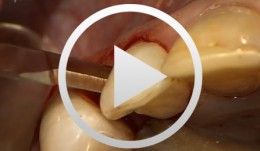

Regenerative Measures for Osseous Defect Repair and Optimal Esthetics
Sculean, AntonProcedure: Theoretical Part: - Adult male with a deep and broad intraosseous bone defect located on tooth #13 - The indication for modified papilla preservation in the scope of regenerative therapy was established based on the width of the diastema - Regenerative periodontal therapy with Emdogain and a Bio-Oss® cancellous bone graft - Emdogain is applied to the root surface to stimulate regeneration of periodontal structures - To prevent graft collapse and to minimize the risk of development of too large a recession in this esthetically important region, the defect was filled with Bio-Oss® cancellous bone material Practical Part: - The papilla preservation technique was performed using microsurgical instruments - The root surface area was conditioned with 24% EDTA for ca. 2 minutes - Emdogain was applied to the root surface - The defect was filled with the Emdogain/Bio-Oss® mixture - The wound was closed with two mattress sutures one horizontal mattress suture to secure the graft in place, and a second modified vertical mattress suture to tightly close the papilla - A 5-0 suture was used for the horizontal mattress suture, and a 6-0 monofilament was used for the vertical mattress suture - Postoperative care entailed rinsing the wound twice daily for 4 weeks with 0.2% chlorhexidine and ibuprofen analgesia on the first few days after surgery Contents: The patient's jaw displayed a generalized loss of clinical attachment and alveolar bone. His general history was unremarkable; the patient was a non-smoker. Microbiological tests showed large numbers of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans and Porphyromonas gingivalis. The diagnosis was "generalized aggressive periodontitis". After four months of initial therapy consisting of antibiotic combination therapy (amoxicillin + metronidazole), intraoral radiographs showed a deep and wide intraosseous bone defect located mesial and palatal to tooth #13. To preserve this strategically important tooth we opted to perform regenerative therapy with Emdogain and Bio-Oss cancellous bone material. Ten months after regenerative periodontal therapy, the probing depth had decreased by 7 mm, and 5-6 mm of clinical attachment had been gained. At this time, the probing depth was 2-3 mm and intraoral radiographs showed near-complete filling of the osseous defect. -


Intraorally Fabricated, Glass Fiber Reinforced Composite Bridge for Replacement of Individual Anterior Teeth - The entire case
Hugo, BurkardProcedure: - Introduction and establishment of indication for the treatment - Bridge construction with glass fiber reinforcement - Presentation of the patient with congenital absence of teeth # 12 and 22 - Clinical procedure for fabrication of a bridge for tooth #22 - Discussion of the technique Contents: Here, we describe a technique for direct application of composite bridges with adhesive bonding. The procedure is designed to provide a replacement for individual anterior teeth, especially in younger individuals who have lost a tooth due to trauma or who have congenitally missing teeth. Bridge manufacture is completely intraoral. By using a one or two-wing abutment design, a framework of parallel, pre-impregnated glass fibers is adhesively bonded, and the midsection is freely built up from composite by a special procedure. This systematic approach permits reasonably priced manufacture of direct tooth replacements with predictably good esthetic results. Maximal conservation of substance and reversibility, which is achieved by dispensing with prepping measures, means that the procedure does not limit the possibilities for future restorations (e.g., implants). -
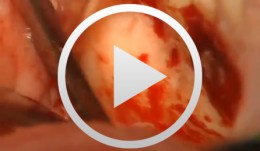

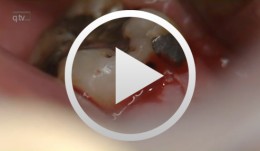
Microsurgical Removal of a Foreign Body from the Mandibular Canal
Schultze-Mosgau, StefanOverview: - Access and incision: Creation of a vestibular pedicled mucoperiosteal flap via a gingival margin incision while preserving the papilla - Removal of vestibular bone in the region of tooth 46 using a microsurgical instrument - Exposure of the neurovascular bundle - Removal of the foreign body - Re-adaptation of the mucoperiosteal flap - Wound closure with atraumatic suture material Contents: Female patient with an indication for microsurgical foreign body removal (removal of a fractured root canal instrument from a previous endodontic treatment of tooth 46) using a surgical microscope. The foreign body extends from the apex into the mandibular canal. -
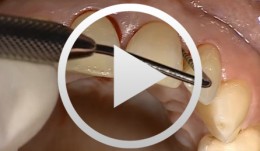

Surgical Treatment of Periodontitis Using a Minimally Invasive Approach
Beck, FrankThis case is an excellent demonstration of the use of the minimally invasive access flap technique for treatment of (chronic) periodontitis in an esthetically critical zone. The access flap was used in conjunction with enamel matrix proteins for regenerative therapy., -

-

SOS - An innovative method for the implantological rehabilitation of the edentulous mandible
Sliwowski, Christoph T. -

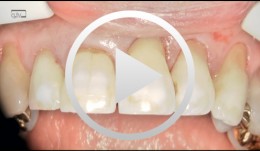
Implant placement in the lower posterior area with immediate provisionalization
Hürzeler, Markus B. -

-


Rational implantation (individual implant in 20 min.)
Bücking, Wolfram