Search results for 'lang'
-
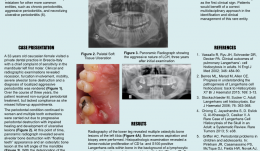

THE ROLE OF MULTIDISCIPLINARY APPROACH IN A CASE OF LANGERHANS CELL HISTIOCYTOSIS WITH INITIAL PERIODONTAL MANIFESTATIONS
Objectives: The present case epitomizes the clinical situation of a single-system Langerhans cell histiocytosis (LCH) mimicking aggressive periodontitis in a patient with no other clinical signs. Although this is a single observation, we highlight the importance of using a multidisciplinary approach in rare conditions like this for optimizing patient management. Methods: A 32-year-old Caucasian woman visited a private dental practice in Brescia, Italy, complaining of sensitivity in her mandibular left first molar. Clinical and radiographic examinations revealed recession, furcation involvement, mobility and severe alveolar bone loss, leading to a diagnosis of localised aggressive periodontitis. Over the next 3 years, the patient received non-surgical periodontal treatment, but failed attend successive follow-up appointments for undisclosed reasons. Her periodontal condition continued to worsen and multiple tooth extractions were carried out due to progressive periodontal destruction with impaired healing and development of ulcerative lesions. Panoramic radiographs were taken, and revealed severe alveolar bone destruction with “floating teeth” appearance, and an osteolytic bone lesion at the left angle of the mandible. With an overall clinical deterioration, and the possibility of an underlying malignant condition, the patient was referred for deep analysis. Results: No abnormalities were detected in laboratory and biochemical tests. Skull and sinus radiography revealed a 5-mm oval radiolucency at the left angle of the mandible. Then a radiograph of the lower leg revealed multiple osteolytic bone lesions of the left tibia. Bone-marrow aspiration and biopsy were performed to determine the nature of these lesions. Histopathology revealed a dense nodular proliferation of CD1a-positive and S100-positive Langerhans cells within bone, on a background of lymphocytic and granulocytic cells, consistent with LCH. An additional biopsy of the intra-oral lesion showed mature, disease-free, compact bone. However, a bone biopsy may be not representative of the entire structure, particularly in cases of intraoral localisation of LCH. Bidirectional Sanger sequencing analysis and pyrosequencing of DNA extracted from bone tissue of the tibia detected the presence of the BRAF-V600E hotspot somatic mutation, confirming a clonal origin of the neoplastic cells. Multidisciplinary investigations showed that the periodontal involvement was a manifestation of an underlying systemic disease (multifocal single-system LCH). The patient was then started on radiotherapy and but improvement of her oral and periodontal condition is yet to be confirmed. Conclusions: In the present case, LCH was unrecognised for several years. The periodontal disease progressed rapidly, leading to loss of most of the dentition, with persistent delays in soft tissues healing after extraction. Close monitoring of the oral signs may have allowed earlier diagnosis of LCH and prevent such rapid deterioration, possibly resulting in a better endpoint. Dentists and periodontists should be aware that rare systemic diseases such as LCH can produce oral manifestations as the first clinical sign. Such patients benefit from a multidisciplinary approach to identify and manage such entities. -
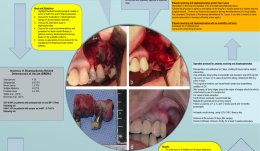

A REVIEW OF BISPHOSPHONATES—POSSIBLE MODES OF ACTION, ALTERNATIVE DRUGS AND IMPLICATIONS FOR DENTAL IMPLANT TREATMENT
Objectives: The review aimed to explore the pharmacophysiological modes of action of both oral and intravenous bisphosphonates and the potential for adverse events in patients receiving dental implant treatment. It aimed to gather evidence on the use of alternative drugs to bisphosphonates, as well as current recommendations and guidelines for dental implant therapy in patients receiving bisphosphonates. It was hoped to devise a clinical protocol for the management of bisphosphonate-treated patients. Methods: A Medline search was conducted to identify articles from the medical and dental literature between 1950 and 31 December 2014 according to well-defined inclusion and exclusion criteria. Searches were made of the Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials and Embase for English-language studies published between 2000 and 31 December 2014. All cited references in the identified papers were cross-checked to ensure that no articles were missed. Given the rarity of studies with a sufficiently large prospective sample to determine the rate of failure (often over 10,000 patients are needed to achieve statistical significance), the heterogeneous studies yielded in this search (in terms of both design and outcome measures) were only suitable for descriptive analysis, rather than a meta-analysis. Results: The initial search of Medline and Embase yielded a total of 37 articles on bisphosphonates and dental implants. On further investigation, only 27 met the study inclusion criteria. There were eight retrospective studies and two case series evaluating the success rate of dental implants in patients with a history of bisphosphonate use, and another 17 articles consisting of case series and case reports. They described incidences of bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaw in dental implant patients. In addition, two relevant articles from the Cochrane Library addressed interventions for treating osteonecrosis of the jaw bone associated with bisphosphonates. A second search of Medline and Embase for “bisphosphonates” (MeSH term) in conjunction with “oral soft tissues”, “oral hard tissues”, “avascular necrosis”, “jaw bone” and “modes/mechanisms of action” yielded a total of 51 English-language studies in humans. Late implant failures are reported in patients treated with oral bisphosphonates for more than 3 years, especially if they have existing integrated implants. Early failures are reported in patients treated with bisphosphonates before or at the time of implant placement. Most organisations agree that a safe approach is the best policy for dealing with patients on oral bisphosphonatess, by assessing the risks on an individual basis and obtaining appropriate consent. This requires close communication with the prescribing physician before surgical intervention. Several alternative drugs are available and their risks profiles also need to be determined in this context. Conclusion: Although many of the studies identified here have shortcomings, there does appear to be some risk associated with both implant placement and maintenance of osseointegrated implants in patients who take oral bisphosphonates. -

Microsurgical lateral sinus floor elevation (LSFE)
Nölken, RobertOutline: - Incision - Flap mobilization - Lateral sinus fenestration - Elevation of the Schneiderian membrane - Implant bed preparation - Bone chip harvesting at the mandibular angle - Filling of sinus lift lumen with autologous bone chips - Implant insertion - Covering the lateral sinus cavity with collagen membrane - Wound closure List of materials - Zeiss Pro Dent microscope with beam splitter and Panasonic 3 CCD camera - Scalpel holder (Ustomed) with Swann-Morton blades 15C and 12D - Narrow rasp (Hu-Friedy) - Micro-vacuum (Luer Lock Suction Tip, American Dental Systems) - Disposable vacuum tube set (Bexamed) - Disposable draping, Lindau (Aescologic) - Piezosurgery with diamond ball (Mectron) - Microforceps (Hu-Friedy) - Excavator (Martin) - Periodontometer, 1-mm gradation (Hu-Friedy) - OsseoSpeed implant set, Dentsply Implants: Marking drill; Twist drill, 2 mm; Depth gauge; Pilot drill, 2/3.2 mm; Twist drill, 3.2 mm; Tapered drill, 3.2/5 mm; OsseoSpeed TX implant, 5.0 × 11 mm; Closure screw, 4.5/5 mm - Columbia curette (Ustomed) - Micross scraper (Meta) - Needle holder (Ustomed) - Langenbeck wound retractor (Ustomed) - Kelly scissors (Ustomed) - Buchanan endodontic hand plugger (American Dental Systems) - Resorbable collagen membrane (Resodont, Resorba) - Ethilon 5-0 FS-3 (Ethicon) - Prolene 6-0 DA-2 (Ethicon) -

Mikrochirurgische laterale Sinusbodenelevation
Nölken, RobertGliederung: - Schnittführung - Lappenmobilisation - Laterale Sinusfensterpräparation - Elevation der Schneiderschen Membran - Implantatbettaufbereitung - Knochenspanentnahme im Unterkieferwinkel - Füllung des Sinuslifts mit autologen Knochenchips - Implantatinsertion - Deckung der lateralen Sinuskavität mit Kollagenmembran - Wundverschluss. Materialliste: - Zeiss Pro Dent Mikroskop mit Strahlenteiler und Panasonic 3 CCD Kamera - Skalpellhalter (Ustomed) mit Swann-Morton Klinge 15C und 12D - Schmales Raspatorium (Hu-Friedy) - Mikrosauger (Luer Lock Suction Tip, American Dental Systems) - Einwegabsaugschlauchset (Bexamed) - Einweg-Abdeckset Lindau (Aescologic) - Piezosurgery mit diamantierter Kugel (Mectron) - Mikropinzette (Hu-Friedy) - Exkavator (Martin) - Parodontometer mit 1 mm-Skalierung (Hu-Friedy) - OsseoSpeed Implantat-Set von Dentsply Implants: Markierungsbohrer; Spiralbohrer 2 mm; Tiefenmesssonde; Pilotdrill 2/3,2 mm; Spiralbohrer 3,2 mm; Konischer Bohrer 3,2/5 mm; OsseoSpeed TX Implantat 5.0 x 11 mm; Verschlussschraube 4.5/5 mm - Columbia Kürette (Ustomed) - Micross Scraper (META) - Nadelhalter (Ustomed) - Wundhaken nach Langenbeck (Ustomed) - Kelly Schere (Ustomed) - Endo Hand-Plugger nach Buchanan (American Dental Systems) - Resorbierbare Kollagenmembran (Resodont von Resorba) - Ethilon 5-0 FS-3 (Ethicon) - Prolene 6-0 DA-2 (Ethicon) -

Innovative Behandlungskonzepte für festsitzenden Zahnersatz auf Implantaten mit Hilfe von CAD/CAM-Technik
Beuer, Florian / Stimmelmayr, Michael / Schweiger, JosefInhalt: - Vorstellung der Patientin - Chirurgische Implantatbettbereitung, Insertion der Implantate, Kontrolle der Implantatposition - Fixierung der Einbringpfosten an der Registrierschablone zur Modellherstellung - Ausführliche Darstellung der Nahtlegung - Einsetzen des angepassten Langzeitprovisoriums - Modellherstellung, Anfertigung einer Zahnfleischmaske, Übertragen des Emergenzprofils der Zwischenglieder auf die Zahnfleischmaske, Anpassen der Zahnfleischmaske - Das Meistermodell unter dem Streifenscanner, mit Scankörpern auf den Laborimplantaten - CAD-Konstruktion einer der Kronen, virtuelles anatomisches Ausformen - CAM-Herstellung eines Abutments aus Zirkoniumdioxidkeramik - Verkleben des Zirkoniumdioxidabutments mit der Titanklebebasis - Wiedereröffnung, Anlage eines Spaltlappens, Vestibulumplastik, Freilegen der Implantate, Fixieren der Zirkoniumdioxidabutments auf den Implantaten - Versorgung eines Weichgewebedefizits mit einem Schleimhauttransplantat - Abformen der Abutments im Mund - Herstellen von Kronen aus Lithiumdisilikatkeramik: virtuelle Konstruktion der Kronen, CAM-Fräsen, Individualisierung der Kronen - Eingliedern, Nachbearbeiten, Vorstellen des Endergebnisses -
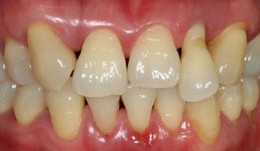

After periodontal therapy an anterior implant supported crown was planed
Prof. Niklaus Lang and J. TamFemale patient *1958, by J. Tam and N. P. Lang (2009-2012). Periodontitis case with mobile and elongated anterior tooth, which was replaced by a single implant crown. -
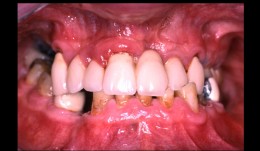

Bilateral reconstruction in a case with gingivitis, FDP on implants
Prof. Niklaus Lang and B. RöthlisbergerMale patient *1943 by B. Röthlisberger, N. P. Lang (2004-2006). Bilateral reconstruction in a case with gingivitis, FDP on implants (2 3-unit FDP, 2 single crowns) -
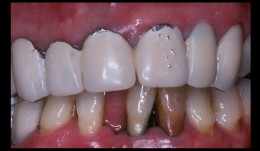

Comprehensive treatment of periodontitis with full mouth reconstruction
B. E. Pjetursson, L. Adriaens, N. P. LangFemale patient *1942 by B. E. Pjetursson, L. Adriaens, N. P. Lang (2004-2006). Comprehensive treatment of periodontitis with full mouth reconstruction. -

Osseointegration
Prof. Niklaus LangProf. Niklaus Lang provides you with the background knowledge of osseointegration, the basis of implant dentistry. He presents and summarizes the relevant animal and human studies on osseointegration, discusses histological evidence and shows impressive documentation of bone formation around dental implants. -
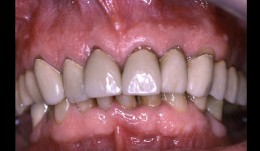

Patient referred has reconstruction in maxilla, shortened dental arch reconstructed
Prof. Niklaus Lang and M. LulicMale patient *1941 by M. Lulic, N. P. Lang (2005-2007). Patient referred has reconstruction in the maxilla, former smoker, shortened dental arch reconstructed with 3 single crowns on implants. -
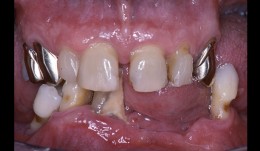

Periodontitis case, fixed reconstructions on implants (bridge and single crown)
Dr. Bjarni E. Pjetursson and Niklaus LangMale patient *1953 by B. E. Pjetursson, N. P. Lang (2001-2003). Periodontitis case, fixed reconstructions on implants (bridges in the mandible and single crown in the maxilla). -
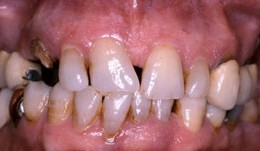

Periodontitis case, fixed reconstructions on teeth and implants
Dr. Matuliene and N. P. LangMale patient *1943, by Matuliene and N. P. Lang (2004-2005). Periodontitis case with mobile tooth and furcation involvement, fixed reconstructions on teeth and implants