-
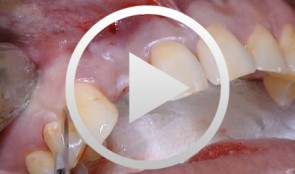

Combined implant treatment with soft and hard tissue management
Schlee, MarkusProcedure - Soft and hard tissue management - Implantodontic treatment - Case documentation Contents: - History - Patient hadn't seen a dentist for 15 years - Has been on Marcumar since developing a blood clot in 1997 - His general practitioner extracted teeth and performed conservative dentistry during the last year - Heavy smoker (30 cigarettes a day) - Prothrombin time (Quick's value): 40 - Premedication: Augmentan 750/125 tablets. -
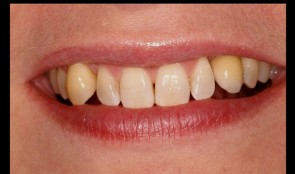

Periodontitis case, smoker, single anterior implant crown
Prof N. P. Lang and M. Lulic.Female patient *1966, by M. Lulic and N. P. Lang (2007-2008). Periodontitis case with pain, smoker, single anterior implant crown. -
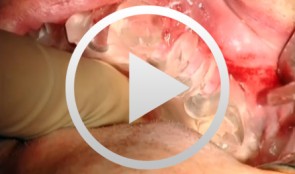

Sinus Bone Augmentation with PRP
Schultze-Mosgau, StefanContents - Incision technique for lateral sinus floor augmentation - Creation of a lateral bone window in the facial maxillary sinus wall - Maxillary sinus floor elevation - Chin bone graft harvesting - Retromolar bone harvesting - Sinus floor augmentation using autologous bone, beta- tricalcium phosphate (1:1) and PRP Synopsis: Maxillary sinus augmentation may be indicated in cases where it is desirable to increase the vertical bone stock in the upper lateral tooth region. Maxillary sinus floor augmentation entails the implantation of autologous bone or bone replacement material in the spaces between the bony floor and elevated membrane of the maxillary sinus. This video demonstrates the techniques for palatal incision, access preparation, and exposure of the facial wall of the maxillary sinus. A diamond drill is used to create a bony window in the facial wall of the maxillary sinus taking care not to perforate the sinus membrane. After completely detaching the basal parts of the membrane, the flap is advanced cranially using angular elevation instruments. Regarding the procedure for autologous bone grafting, the steps for incision, prepping and harvesting of monocortical chin bone transplants with a trephine drill are demonstrated. An alternative procedure for harvesting retromolar bone material is also shown. A bone mill is used to particulate the autologous bone material. The autologous bone chips are then mixed 1:1 with beta-tricalcium phosphate (and PRP) and inserted in the sinus floor. -
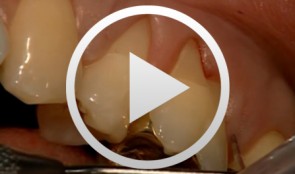

Regenerative Therapy for Multiple Recessions
Heinz, BerndContents - History - Emdogain Application - Incision - Periosteal Incision - Root Smoothing - Suture Technique - PrefGel Application Synopsis: Regenerative periodontal surgery with Emdogain enamel matrix protein: The goal of regenerative periodontal surgery is to rebuild destroyed periodontal structures. Bone transplants, bone replacement materials, and nonresorbable and resorbable membranes have been and still are being used. In a new therapeutic approach to periodontal regeneration, the root surface is conditioned using an enamel matrix protein derivative (Emdogain, Biora). The protein complex stimulates the regeneration of root cement, which in turn leads to the regeneration of bone and collagen fibers. Since the early 1980's, Professor Lars Hammerström's Swedish research team has performed extensive research and studies on this method and its mode of action. Emdogain is now used for treatment of vertical bone defects and furcation defects. The exposed root surface is first carefully scaled using handheld instruments or a rotating, fine-grain diamond drill. PrefGel EDTA suspension (Biora) is then applied for 2 minutes, then thoroughly rinsed with physiological saline solution. The EDTA suspension serves to remove the smear layer and opens the dentinal tubules, leading to improved binding of Emdogain to the root surface. Emdogain is applied to the blood- and saliva-free root surface immediately after rinsing. Finally, the wound is sutured closed. -
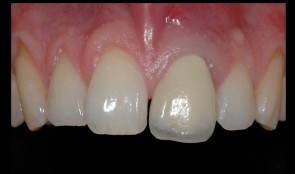

Replacement of central incisor with implant and closure of diastema
PD Dr. Ronald JungThe broken central incisor 21 was replaced with an implant-supported crown. The diastema could be closed with an etch-piece on 11. -
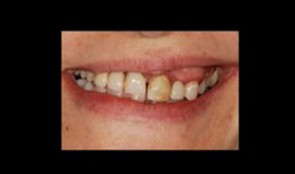

Replacement of poorly fitting removable prosthesis and simultaneous orthodontic treatment
Dr. Dominik BüchiThis patient (*1971) treated by Dr. Büchi, came to our clinic for a replacement of her poorly fitting removable prostheses. Additionally severe orthodontic problems, i.e. a slanting occlusion plane are bothering the patient and are in need of treatment. -
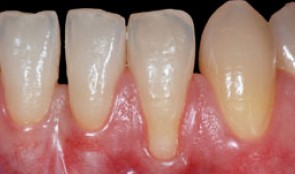

Root coverage with tunnel technique
Ignacio Sanz MartinRecession on tooth 32. Connective Tissue graft with tunnel technique for root coverage. -

Single implant crown in the esthetic zone
Dr. Vladimir KokovicMale patient *1986 by Dr. V. Kokovic (02-10/2007). Anterior single implant placement after orthodontic extrusion and ridge preservation. -

Tendency of skeletal class 3 and a missing front tooth
Dr. Dominik BüchiIn this clinical case session you are going to learn how to plan and execute treatment in a partially edentulous patient situation applying implants within the overall reconstructive treatment concept. In particular you will learn the importance of the preparatory phases of therapy and to plan and treat with the prosthetic aim in mind. -
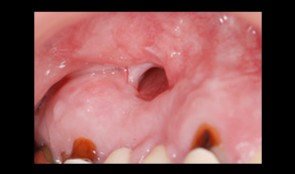

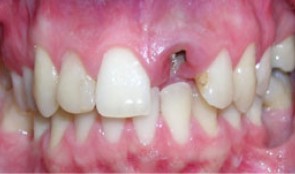
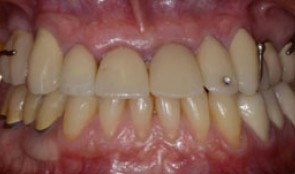
Total reconstruction after closure of maxillary sinus fistula
Dr. Thomas TruningerBefore starting the full-mouth reconstruction, the oral-maxillary sinus fistula (oroantral fistula) has to be closed.