-
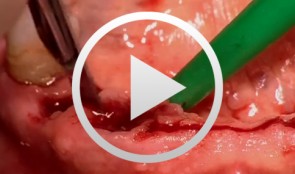

Treatment of the Edentulous Mandible with an Immediately Loaded Screw-retained Fixed Restoration - The entire case
Yüksel, OrcanProcedure: - Presentation of procedure for immediate implant loading in the edentulous mandible according to the Ledermann concept - Surgical implantation of XIVE® TG implants - Bite registration and impression-taking - Presentation of prosthetic components - Fitting and passive fixation of the mesostructure in the mouth - Integration procedure Contents: This video demonstrates the extraction of teeth in a partially dentate mandible followed by immediate loading of six XIVE® TG implants. Following the Ledermann immediate loading concept, a mesostructure will be used for tension-free primary interlock in this special case. Bridge-like lower full dentures with plastic teeth will then be inserted on this frame and retained with an occlusal screw. Since the dentures can only be removed by the dentist, they are \fixed\ as far as the patient is concerned. This simple and quickly produced yet extremely well-fitting restoration, which requires only minimal time and effort for the implant components, is the subject of this contribution. -


Minimally Invasive Implant Surgery based on Three-Dimensional CT Treatment Planning for Total Rehabilitation
Beck, FrankProcedure: - Incision Technique 36, 44 - Gentle Flap Mobilization - Pilot Hole Preparation using a CT Template - Sequential Preparation and Implantation - Bone Removal and Augmentation - Wound Closure Contents: Systematic Total Rehabilitation is very challenging, especially in patients with Periodontal Disease with Loss of Supporting Structures. Precise Treatment Planning is essential. The Treatment of Periodontal Disease begins after Conservative Pretreatment. It is not possible to predict the Soft Tissue Esthetic Outcome before the Healing Process is completed. We selected Endosteal Implants for the Augmentation of Lost Support Zones in this Atrophic Mandible. A Three-Dimensional Analysis was performed as the Basis for Navigated Implantation. After Completion of the Periodontal Treatment and Implantation, the patient must wait for approximately 6 months for the Completion of the Healing Process before Prosthetic Reconstruction Procedures can be initiated. -
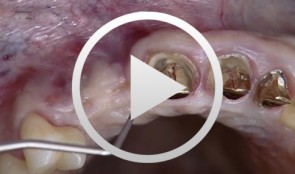
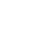
Implantation with Simultaneous Augmentation
Grunder, UeliProcedure: - Case evaluation - Incision technique - Implant placement - Membrane adjustment and fixation - Introduction of replacement material - Flap mobilization - Suture technique Contents: Implantation was desired for replacement of a missing upper canine tooth and the adjacent lateral incisor tooth. The initial case evaluation revealed a relatively narrow gap between these two teeth in addition to extensive hard and soft-tissue defects. We selected an incision technique that made it possible to do the augmentation work yet subsequently achieve a tension-free flap closure. Since the bony defect was large while the available space was limited, we had to go for the best possible compromise in regard to implant insertion. After the implants had been inserted, augmentation was carried out using a non-absorbable, titanium-reinforced membrane, bone replacement material, and an absorbable membrane. Extreme flap mobilization was needed to achieve flap closure. An optimal suture technique was used to complete the surgery. -
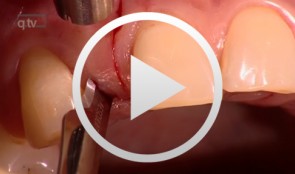

Single Tooth Replacementwith Implants in the Esthetic Region
Yüksel, OrcanProcedure: Delayed loading of dental implants in the esthetic zone of the maxilla. Guided bone regeneration (GBR) for compensatory augmentation with subsequent exposure after healing. Contents: Soft and hard tissue loss leads to esthetic problems, even in patients with successful implant osseointegration. Delayed loading of dental implants in the esthetic zone is frequently indicated in dental practice, for example, in patients with congenital absence of the lateral incisors. Dental implants can solve this problem. Depending on the extent of hard tissue loss, it may be necessary to perform guided bone regeneration (GBR) in order to achieve better esthetic results. Depending on the degree of atrophy, GBR may be performed before or simultaneous with implantation. Correct implant placement is essential to achieving the end goal: an esthetically pleasing and natural result. In this film and in the presentation, we will demonstrate in detail the procedure for placing implants in this esthetically sensitive region. In addition, we will demonstrate a method of impression-taking that provides dental laboratories a better foundation for achieving excellent esthetic results. -
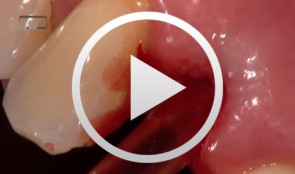

Single Tooth Replacement of an Upper Lateral Incisor
Wagner, WilfriedProcedure: - Extraction - Implant Site Drilling and Implant Placement - T-Adapt Insertion Contents: This live operation starts with the extraction of tooth 12, which was loosened and damaged by trauma. Pin fixation was not possible, and a significant loss of distal papillary substance was observed. We therefore elected for placement a 4.5 mm conical Astra implant. After completion of the implant site drilling and the implant placement, a T-Adapt was inserted to shape and support the mucosa. A temporary crown was inserted chairside and left in place for 3 months. -
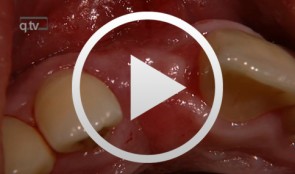

Anterior Implant Placement using in a Combined Roll Flap and Connective Tissue Graft Technique
Schultze-Mosgau, StefanProcedure: - Incision Technique and Roll Flap Creation - Excision and Transplantation of Connective Tissue Graft Material from the Palate - Implant Placement and Fixation Procedure Contents: This video describes the preparation of an implant insertion site for placement of an individual implant at site 11 using a roll flap and free connective tissue graft technique. The procedure is designed to shape the implant insertion site and to create a secure, keratinized gingival base. Step-by-step, the operator demonstrates the incision technique, the roll flap creation procedure and the techniques used for excision, transplantation and fixation of the free connective tissue graft within the scope of implant placement. -


Immediate Implant Placement in the 12 and 22 Region
Diemer, JosefProcedure - Incision in region 22 - Flap Design - Preparation of the Implant Bed - Implant Placement - Suture - Extraction of tooth 12 - Curretage - Implant Placement Materials Implant System: 3I, Osseotite, Ø 4mm Region 12: 15mm length Region 22: 13mm length -


Prosthetic Planning and Prosthetically Guided Minimally Invasive Implantation
Rammelsberg, Peter / Hassel, AlexanderContents: - Considerations for prosthetic treatment planning (PowerPoint) - Production of the drill guide according to prosthetic specifications (PowerPoint) - Surgical procedure (film) - Flapless surgery - Access preparation - Pilot drilling using the drill guide - Preparation of the implant site - Internal sinus lift - Implantation Materials Checklist: Pilot drill; Alignment pin, depth gauge Straight osteotome for bone condensation (Ø 3.5 mm); Larger drills to enlarge the osteotmy; Round burs; Osteotome, angled, for sinus lift (Ø 4.2 mm); Ratchet, adaptor for ratchet (short); Holding key for transmission, SCS screwdriver (short); STRAUMANN Standard Plus RN implant (Ø 4.1 mm, L: 12 mm) and healing abutment (2 mm); STRAUMANN Standard Plus WN implant (Ø 4.8 mm, length 12 mm) and healing abutment (3 mm); Scalpel blade (15c) and scalpel blade holder (Martin); Two dental mirrors and dental forceps; Surgical forceps; Anatomical forceps; Probe; Periodontal probe; Sharp spoon; Sterile compresses (Hu Friedy); Isotonic sodium chloride solution, 0.9% (Braun). -

-
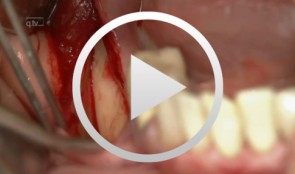

Sandwich osteotomy in the posterior mandible
Bormann, Kai-Hendrik