-
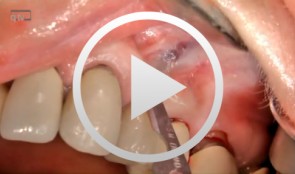

-
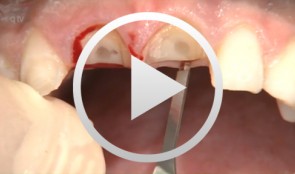

Socket-shield surgery on two central incisors
Hürzeler, Markus B. -


Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry - Esthetic Post Systems
Terry, Douglas A. -
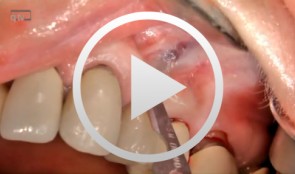

Microsurgical apical resection on a maxillary premolar
Nölken, Robert -


Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry - Dental Photography
Terry, Douglas A. -


Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry - The Impression Process
Terry, Douglas A. -
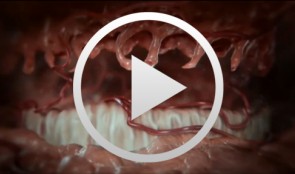

Cell-to-Cell Communication: Periodontal Regeneration
Stadlinger, Bernd / Terheyden, HendrikUnlike bone, which undergoes remodeling by resorption followed by bone apposition, teeth are not subject to physiological remodeling. They are remarkably resistant to physiological remodeling processes. The reason for this is found in the periodontium and cementum. The mechanisms that take effect in this area and the effectiveness of the periodontal system - consisting of gingiva, alveolar bone, periodontium and cementum - after injuries will be visualized in the new scientific 3D film, "Periodontal Regeneration".The visualization of these complex processes is of great interest for academic teaching as well as for the clinician and general practitioner as the cellular interactions are presented in the context of four phases. For the first time scanning electron microscopic images of real cells will be visualized allowing the comparison of their characteristics with computer animated simulations. DVD 1: Expert Version approx. 14 minutes DVD 2: Public Version approx. 13 minutes Outline: - Cementum formation - Orthodontic tooth movement - Trauma and periodontitis - Periodontal regeneration -
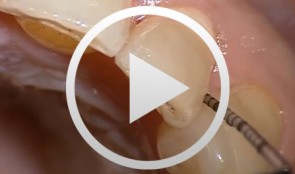

Minimally Invasive Treatment of Periodontitis (Surgical Treatment of Recurrences)
Beck, FrankContents: When treating recurrent periodontitis surgically, the challenge is to sacrifice as little soft tissue as possible in esthetically critical areas. This surgical case demonstrates the technique used in patients with narrow approximal spaces. -
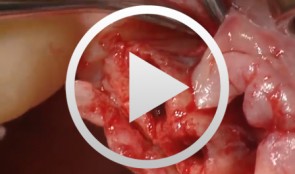
Bone Spreading, Bone Condensing
Streckbein, RolandContent: Surgical flap creation and elevation; Use of drill template for exact determination of implant position; Implant site creation; Site preparation / tapping; Bone compaction; Insertion of the implants; Impression-taking; Wound closure; Later implant insertion; Dental lab work; Creating the model with laboratory implants; Shaping the bar frame; Adapting the laser welded frame to the model; Manufacturing the tooth replacement, Fitting the bar into the tooth replacement; Finishing work. -
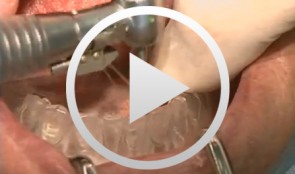

Implants for the Anterior Maxillary Region
Horrichs, Leon G.Contents: - Implant planning and positioning - Preparation - Drilling and thread-cutting - Implant insertion - Wound closure Synopsis: The implant position is determined using a drill guide/x-ray template (regions 34-32-42-44). A Peeso drill is inserted in the drill guide and used to mark the position in the mucoperiosteum. An incision is made, and the mucoperiosteum is displaced. The implant insertion sites are prepared by using a 2 mm twist drill, 2/3 mm pilot drill, 3 mm and 3/5 mm twist drills. This is followed by counter-drilling and thread-cutting. The implants were loaded at 40-50 N. The wound is then closed using GORE-TEX® suture material.