-
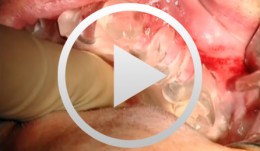

Sinus Bone Augmentation with PRP
Schultze-Mosgau, StefanContents - Incision technique for lateral sinus floor augmentation - Creation of a lateral bone window in the facial maxillary sinus wall - Maxillary sinus floor elevation - Chin bone graft harvesting - Retromolar bone harvesting - Sinus floor augmentation using autologous bone, beta- tricalcium phosphate (1:1) and PRP Synopsis: Maxillary sinus augmentation may be indicated in cases where it is desirable to increase the vertical bone stock in the upper lateral tooth region. Maxillary sinus floor augmentation entails the implantation of autologous bone or bone replacement material in the spaces between the bony floor and elevated membrane of the maxillary sinus. This video demonstrates the techniques for palatal incision, access preparation, and exposure of the facial wall of the maxillary sinus. A diamond drill is used to create a bony window in the facial wall of the maxillary sinus taking care not to perforate the sinus membrane. After completely detaching the basal parts of the membrane, the flap is advanced cranially using angular elevation instruments. Regarding the procedure for autologous bone grafting, the steps for incision, prepping and harvesting of monocortical chin bone transplants with a trephine drill are demonstrated. An alternative procedure for harvesting retromolar bone material is also shown. A bone mill is used to particulate the autologous bone material. The autologous bone chips are then mixed 1:1 with beta-tricalcium phosphate (and PRP) and inserted in the sinus floor. -
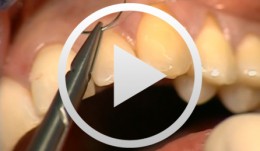

Esthetic Periodontal Treatment with Microsurgical
Wachtel, HannesContents - Instruments and planning - Incision - Split thickness flap preparation - Harvesting connective tissue for grafting - Palatal sutures - Transplant insertion and suture - Microsurgical suture Synopsis: Microsurgical operation to repair two adjacent, exposed root surfaces. The video demonstrates step-by-step how to prepare a coronally advanced split-thickness flap with subepithelial connective tissue. To remove connective tissue from the palate, a horizontal incision is required. Ultra-precise microsurgical suturing is the key to obtaining aesthetically perfect results. -
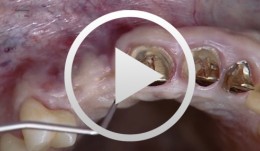
Implantation with Simultaneous Augmentation
Grunder, UeliProcedure: - Case evaluation - Incision technique - Implant placement - Membrane adjustment and fixation - Introduction of replacement material - Flap mobilization - Suture technique Contents: Implantation was desired for replacement of a missing upper canine tooth and the adjacent lateral incisor tooth. The initial case evaluation revealed a relatively narrow gap between these two teeth in addition to extensive hard and soft-tissue defects. We selected an incision technique that made it possible to do the augmentation work yet subsequently achieve a tension-free flap closure. Since the bony defect was large while the available space was limited, we had to go for the best possible compromise in regard to implant insertion. After the implants had been inserted, augmentation was carried out using a non-absorbable, titanium-reinforced membrane, bone replacement material, and an absorbable membrane. Extreme flap mobilization was needed to achieve flap closure. An optimal suture technique was used to complete the surgery. -
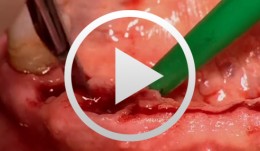

Treatment of the Edentulous Mandible with an Immediately Loaded Screw-retained Fixed Restoration - The entire case
Yüksel, OrcanProcedure: - Presentation of procedure for immediate implant loading in the edentulous mandible according to the Ledermann concept - Surgical implantation of XIVE® TG implants - Bite registration and impression-taking - Presentation of prosthetic components - Fitting and passive fixation of the mesostructure in the mouth - Integration procedure Contents: This video demonstrates the extraction of teeth in a partially dentate mandible followed by immediate loading of six XIVE® TG implants. Following the Ledermann immediate loading concept, a mesostructure will be used for tension-free primary interlock in this special case. Bridge-like lower full dentures with plastic teeth will then be inserted on this frame and retained with an occlusal screw. Since the dentures can only be removed by the dentist, they are \fixed\ as far as the patient is concerned. This simple and quickly produced yet extremely well-fitting restoration, which requires only minimal time and effort for the implant components, is the subject of this contribution. -
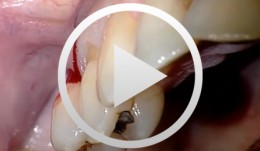

Piezo Surgery Technique for Alveolar Ridge Augmentation with Sinus Lift
Schlee, MarkusOverview: - Periodontal and implant planning - Treatment of a horizontal and vertical bone defect - discussion of the literature - Clinical implementation of bone augmentation using a bone block and treatment of a vertical pocket with Emdogain - Sinus lift in combination with alveolar ridge augmentation and horizontal expansion of the alveolar process; orthodontic straightening of a molar tooth Contents: This contribution illustrates a complex periodontal-implantological case, from treatment planning to clinical implementation. It details the transplantation of two bone blocks from the linea obliqua of the angle of the jaw to the anterior front tooth region, the treatment of a vertical bone pocket with Emdogain, the straightening of a molar tooth using orthodontic mini-implants, and a sinus lift together with alveolar ridge augmentation in the maxillary region using a piezo surgical technique. -
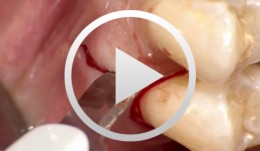

Guided Bone Regeneration in Posterior Maxilla with Membrane Technique. Insertion of an Implant - The entire case
Mengel, Reiner / Foitzik, ChristianOverview: Part 1 - Incision and mobilization of the mucoperiosteal flap - Cleaning the bony defect - Screw insertion for support, membrane application and fixation - Suture closure Part 2 - Opening of the mucosa above the region of augmented bone - Preparation of tunnel and bone bed for an open screw-type endosteal implant (Straumann® implant) - Use of single button sutures for tension-free wound closure Contents: This female patient presented with bone loss due to a radicular cyst at tooth 27 and peri-implantitis at tooth 26. Four months after extraction of the respective tooth and implant, guided bone regeneration (GBR) was carried out using supporting screws and an e-PTFE membrane for augmentation of the posterior tooth region of the maxilla. Four months after GBR the insertion of an implant took place. -

Multiple recession coverage using a modified tunnelling procedure
Zuhr, OttoOverview - Incision technique - Flap creation - Transplant fixation - Suture closure Contents: This video demonstrates the coverage of multiple recessions by means of a modified tunneling technique characterized by the use of a minimally invasive, atraumatic procedure without the creation of vertical incisions -
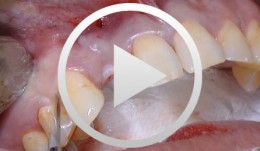

Combined implant treatment with soft and hard tissue management
Schlee, MarkusProcedure - Soft and hard tissue management - Implantodontic treatment - Case documentation Contents: - History - Patient hadn't seen a dentist for 15 years - Has been on Marcumar since developing a blood clot in 1997 - His general practitioner extracted teeth and performed conservative dentistry during the last year - Heavy smoker (30 cigarettes a day) - Prothrombin time (Quick's value): 40 - Premedication: Augmentan 750/125 tablets. -
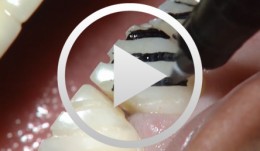

Restoration of Anterior Teeth with Porcelain laminate Veneers
Bastek, Siegfried / Fiechter, PaulContent: Preparation of teeth; Composite build-up for larger lesions; Smoothing of preparation surfaces; Placement of retraction cords; Impression-taking with A-silicone; Placement of temporary; Preparation of model; Preparation of laminate veneers; Final adhesive bonding of laminate veneers. -


Bone Transfer
Streckbein, RolandContent: Description of system and instruments. The patient had a considerable bone deficit at tooth 21. Augmentation was therefore required and was carried out using calibrated instruments. The augmentation site was prepared using instruments that matched the tools used to harvest the cylindrical bone graft at the donor site. This perfect match between the augmentation region and the bone transplant accelerated osseointegration, there by shortening the required waiting time for implant placement. -
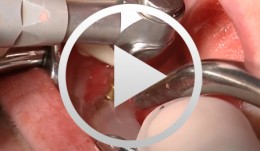

Implant-borne Immediate Prothesis on Laser-Welded Bar
Drobig, FelixDescription of baseline situation; Exposure of underlying bone; Insertion of four implants; Impression-taking; Bar construction; Welding the individual components, Correction of tension; Finishing the bar; Adjusting the prosthesis; Implant placement. -
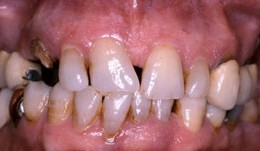

Periodontitis case, fixed reconstructions on teeth and implants
Dr. Matuliene and N. P. LangMale patient *1943, by Matuliene and N. P. Lang (2004-2005). Periodontitis case with mobile tooth and furcation involvement, fixed reconstructions on teeth and implants