Free content
-
-
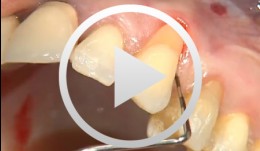

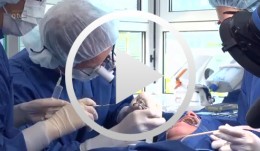
Covering a Recession with a Soft Tissue Transplant
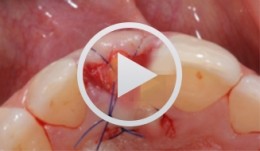
Heinz, Bernd / Jepsen, SörenObjectives: Use of a soft tissue graft for recession coverage at tooth 23 and for gingival augmentation. Content: 1. Incision around tooth 23, intra-sulcular preparation, mobilization of coronal sliding flap, and pre-flap preparation. 2. Root smoothing, reduction of ground cavity with diamond burs from Perioset system. 3. Preparation and harvesting of connective tissue flap from palate, Emdogain application, and wound closure. 4. Placement of interrupted interdental sutures for fixation of connective tissue flap. -


Short and narrow implants, how far can we go?
Christoph Hämmerle, José NartIn this webinar moderated by Prof Ronald Jung and Dr. Adrián Guerrero the expert presenters Prof. Christoph Hämmerle and Dr. José Nart discuss about the importance and benefits of using short and narrow implants. -
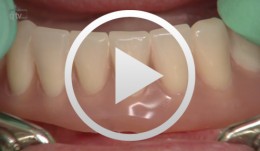

Fiberglass frameworks in removable prosthodontics
Bücking, Wolfram -

-

Soft Tissue Management in the Aesthetic Zone
Daniel ThomaExpert presenter PD Dr. Daniel Thoma is a Head of Academic Unit at the Clinic for Fixed and Removable Prosthodontics and Dental Material Sciences, University of Zurich, Switzerland. Long-term successful outcomes with implant therapy are based on a number of parameters. Among these, the critical assessment of the peri-implant soft tissues and subsequent therapeutical interventions are considered key factors. -


Cell-to-Cell Communication - Inflammatory Reactions
Stadlinger, Bernd / Terheyden, HendrikVisualizing the invisible while experiencing a fascination with science is the great challenge that Cell-to-Cell Communication, representing an all-new genre, has set out to meet. A spectacularly sophisticated computer animation in HD quality depicts the highly complex processes of intercellular interaction during an inflammatory periodontal reaction complete with the messenger molecules implicated. The various cell types constitute the main cast of the film, using a finely tuned communication process in their quest to destroy the bacterial invaders, with messenger molecules as supporting cast. A stunning didactic and dramatic experience! Outline: - Biofilm - Gingivitis and the Innate Immune Defense - Periodontitis and the Adaptive Immune Defense - Cleaning and Regeneration -

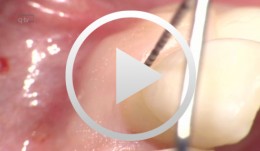
REAL-TIME NAVIGATION: THE BEGINNING OF A NEW ERA IN GUIDED IMPLANT SURGERY
Objectives: To demonstrate that dynamic guided surgery is as predictable as conventional surgery. Methods: Partially edentulous patients requiring a fixed rehabilitation were selected for this pilot study. No specific contraindications were established, and smokers were not excluded. An impression was taken pre-operatively using an irreversible hydrocolloid (Cavex CA37®) to fabricate a diagnostic cast for moulding the surgical stent (NaviStent®). Afterwards, a standard cone-beam CT (CBCT) scan was made with the NaviStent® in place using a Planmeca Promax 3-D Max®. Images were converted into DICOM files and transformed into a 3-D virtual model using the Navident® software. The potential implant locations were planned in a prosthesis-driven way. For preparing the osteotomy, the drilling axis of the handpiece and the twist drills were calibrated. The osteotomies were prepared at low speed using a high level of cooling. The navigation software guided the drilling procedure in real time. Before installing implants, an extra calibration procedure was performed for tracking the implant. The aim of this pilot study was to determine the clinical outcome up to 12 months post-operatively for implants installed using the Navident® guided surgery system. Results: Partially edentulous men (n = 6) and women (n = 7) were included in this pilot study (mean age 52.15 years; range 20–75). Out of these 13 patients, two were current smokers of more than 10 cigarettes per day. Twenty implants were inserted. No mechanical or biological complications occurred during the surgical procedure, and no major complaints were reported, such as hemorrhage, sinus pathology or severe post-operative pain. No implants were lost up to 1 year after insertion, resulting in 100% implant survival. Conclusions: Based on the results of this pilot study, real-time navigation is a promising technique. However, there is not yet enough evidence to show that the method is as safe and predictable as conventional implant surgery. -

-
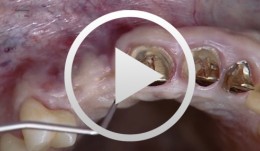

Implantation with Simultaneous Augmentation
Grunder, UeliProcedure: - Case evaluation - Incision technique - Implant placement - Membrane adjustment and fixation - Introduction of replacement material - Flap mobilization - Suture technique Contents: Implantation was desired for replacement of a missing upper canine tooth and the adjacent lateral incisor tooth. The initial case evaluation revealed a relatively narrow gap between these two teeth in addition to extensive hard and soft-tissue defects. We selected an incision technique that made it possible to do the augmentation work yet subsequently achieve a tension-free flap closure. Since the bony defect was large while the available space was limited, we had to go for the best possible compromise in regard to implant insertion. After the implants had been inserted, augmentation was carried out using a non-absorbable, titanium-reinforced membrane, bone replacement material, and an absorbable membrane. Extreme flap mobilization was needed to achieve flap closure. An optimal suture technique was used to complete the surgery. -

Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry - Ceramic Materials
Terry, Douglas A. -
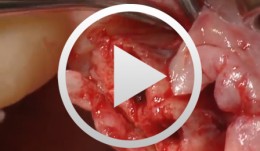

Bone Spreading, Bone Condensing
Streckbein, RolandContent: Surgical flap creation and elevation; Use of drill template for exact determination of implant position; Implant site creation; Site preparation / tapping; Bone compaction; Insertion of the implants; Impression-taking; Wound closure; Later implant insertion; Dental lab work; Creating the model with laboratory implants; Shaping the bar frame; Adapting the laser welded frame to the model; Manufacturing the tooth replacement, Fitting the bar into the tooth replacement; Finishing work. -
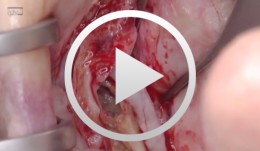

Live surgery Surgical treatment of bone necrosis
Schultze-Mosgau, StefanOutline: - Surgical wound debridement - Sequestrotomy - Preparation of the soft-tissue bed - Plastic, tension-free, saliva-proof wound closure List of materials Basic surgical tool set: - Surgical blade - Preparation scissors - Pair of tweezers - Suture materials -


-
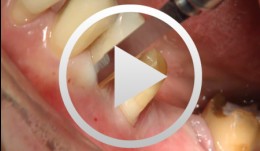

Periodontal Preserve Therapy (Examples)
Clotten, StefanContent: - Periodontal maintenance therapy for teeth 34 and 35, including the regeneration of a bone defect using bone replacement material, collagen membrane and sutures. - Curettage for treatment of periodontal pockets. - Treatment of gingival pressure sores caused by tight-fitting orthodontic apparatus. - Incision of buccal attachment to relieve gingival pressure for elimination of gingival recession. -
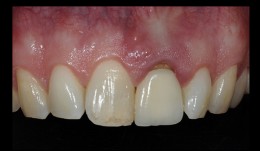

Aesthetic upper anterior implant placement case
Dr. Dominik BüchiDr. Dominik Büchi performed a ridge preservation to keep the soft tissue volume. He then placed an implant 8 weeks later with simultaneous GBR. The final emergence profile was created by a fixed provisional crown.
Most Popular
-


Minimally Invasive Implant Surgery based on Three-Dimensional CT Treatment Planning for Total Rehabilitation
Beck, FrankProcedure: - Incision Technique 36, 44 - Gentle Flap Mobilization - Pilot Hole Preparation using a CT Template - Sequential Preparation and Implantation - Bone Removal and Augmentation - Wound Closure Contents: Systematic Total Rehabilitation is very challenging, especially in patients with Periodontal Disease with Loss of Supporting Structures. Precise Treatment Planning is essential. The Treatment of Periodontal Disease begins after Conservative Pretreatment. It is not possible to predict the Soft Tissue Esthetic Outcome before the Healing Process is completed. We selected Endosteal Implants for the Augmentation of Lost Support Zones in this Atrophic Mandible. A Three-Dimensional Analysis was performed as the Basis for Navigated Implantation. After Completion of the Periodontal Treatment and Implantation, the patient must wait for approximately 6 months for the Completion of the Healing Process before Prosthetic Reconstruction Procedures can be initiated. -

-
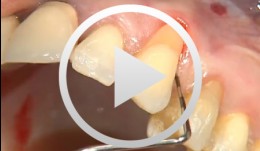

Abdeckung einer Rezession mittels Bindegewebstransplantat
Heinz, Bernd / Jepsen, SörenZielsetzung: Rezessionsdeckung an Zahn 23 und Verstärkung der Gingiva durch ein Bindegewebstransplantat. Inhalt: 1. Schnittführung in regio 23, intrasulkuläre Präparation, Mobilisation der Koronalverschiebelappen, Präparation eines Vorflap. 2. Wurzelglättung, Reduktion der Grundkavität mit Diamanten aus dem Perioset-System. 3. Präparation und Entnahme des Bindegwebstransplantats aus dem Palatinum, Applikation von Emdogain und Wundverschluss. 4. Fixierung und Vernähen des Bindegewebstransplantats durch interdentale Knopfnähte.
Recommended to You
-


HYBRID SCAFFOLDS COMPOSED OF BETA-TRICALCIUM PHOSPHATE (TCP), poly (D,L- lactic acid) (PDLLA) AND COLLAGEN FOR ALVEOLAR BONE AUGMENTATION
Objectives: Dimensional changes occur in the alveolar ridge after tooth loss, due to bone resorption. Bioactive ceramic scaffolds are available for bone alveolar augmentation, but their mechanical properties are still an issue during implantation. The aim of this study was to characterize the mechanical properties of synthesized β-TCP hybrid scaffolds coated with bioabsorbable collagen or PDLLA. Methods: β-TCP powder was obtained by reactive milling. Scaffolds were produced by the replica method from polyurethane foam patterns. Type I collagen or poly (D,L- lactic acid) (PDLLA) were used to coat the scaffolds by dip coating. The hybrid scaffolds were then divided into four groups: non-coated (GA); double immersion in collagen type I (GB); double immersion in PDLLA (GC); and ten immersions in PDLLA (GD). Samples were characterized by compressive tests, x-ray diffraction and scanning electron microscopy with energy dispersive x-ray analysis (SEM/EDS). Statistical analysis was performed by two-way ANOVA(p Results: Chemical and microscopic analyses revealed proper morphology of powder particles and scaffolds with or without polymeric coatings. Hybrid scaffolds of PDLLA had higher compressive strength (0.11 MPa ± 0.054) (p Conclusion: β-TCP scaffolds synthesised by the replica method showed proper morphology and size of interconnected pores. The PDLLA scaffold-coating method increased mechanical strength of the porous ceramic material, showing desirable properties such as high compressive strength, biocompatibility and osteoconductivity. These properties are essential in alveolar preservation procedures for resisting compression from soft tissues and occlusal stress from mastication. -


Osteology Research Wizard
Are you about to start your scientific career and you have a research question in mind, but no idea how to start a project?The Research Wizard guides you step by step in the process of drafting a new research project and directs you to important information. -

Esthetic Periodontal Treatment with Microsurgical
Wachtel, HannesContents - Instruments and planning - Incision - Split thickness flap preparation - Harvesting connective tissue for grafting - Palatal sutures - Transplant insertion and suture - Microsurgical suture Synopsis: Microsurgical operation to repair two adjacent, exposed root surfaces. The video demonstrates step-by-step how to prepare a coronally advanced split-thickness flap with subepithelial connective tissue. To remove connective tissue from the palate, a horizontal incision is required. Ultra-precise microsurgical suturing is the key to obtaining aesthetically perfect results.